การค้นหาโดยอัตโนมัติของภาวะเบาหวานขึ้นจอตาจากภาพถ่ายจอประสาทตา
คณะเทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศและการสื่อสาร มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล


{:th}
การค้นหาโดยอัตโนมัติของภาวะเบาหวานขึ้นจอตาจากภาพถ่ายจอประสาทตา
คณะเทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศและการสื่อสาร มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล
โครงการวิจัย:
การค้นหาภาวะเบาหวานขึ้นจอตาด้วยเทคนิคการประมวลผลภาพ
ผลงานวิจัย:
การค้นหาโดยอัตโนมัติของภาวะเบาหวานขึ้นจอตาจากภาพถ่ายจอประสาทตา
ผู้วิจัย:
ผศ. ดร.วรพันธ์ คู่สกุลนิรันดร์
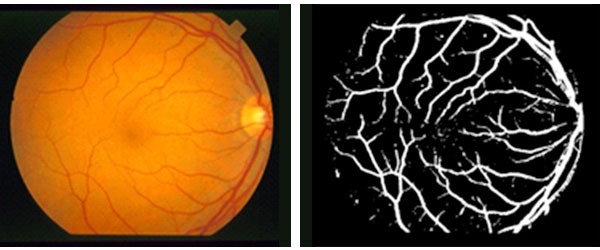
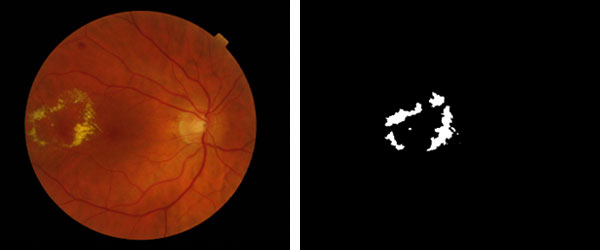
โครงการวิจัยนี้ มีวัตถุประสงค์หลักในการพัฒนาวิธีการและโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์ ในการค้นหาและแบ่งระดับความรุนแรงของโรคเบาหวานขึ้นจอตาในภาพถ่ายจอประสาทตา ในรูปแบบอย่างเป็นอัตโนมัติ เพื่อที่จะสามารถช่วยในการคัดกรองภาพถ่ายจอประสาทตา สำหรับระดับความรุนแรงขั้นต้นที่สามารถรักษาให้หายขาดได้ หรือระดับความรุนแรงของโรคที่ต้องการการช่วยเหลืออย่างเร่งด่วน เพื่อไม่ให้เข้าสู่ภาวะการเสียการมองเห็น การมีโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์ที่สามารถค้นหาโรค และวิเคราะห์ระดับความรุนแรงได้อย่างอัตโนมัติ จะสามารถช่วยให้การตรวจภาพถ่ายจอประสาทตาเข้าถึงคนไทยได้มากขึ้น โดยเฉพาะในบริเวณที่ห่างไกลสถานพยาบาล การพัฒนาในโครงการนี้ ใช้วิธีการประมวลภาพขั้นสูงในการแยกพื้นที่ภาพที่สามารถระบุระดับความรุนแรงได้ เช่น Microaneurysms, Hard Exudates และ Abnormal Blood Vessels ซึ่งสามารถใช้ต่อในการวิเคราะห์และประมวลผลการแยกระดับความรุนแรง โดยใช้การเรียนรู้ด้วยตัวเองของคอมพิวเตอร์ หรือ Machine Learning และในอีกส่วนของการพัฒนา คือ การใช้เทคนิคการเรียนรู้เชิงลึก เพื่อเรียนรู้ลักษณะของโรคเบาหวานขึ้นจอตาในแต่ละระดับ เพื่อให้สามารถแยกภาพถ่ายจอประสาทตาได้ วิธีการและโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์ที่พัฒนาขึ้นมา ได้ทำการวัดประสิทธิภาพในทั้งมุมมองของการแยกพื้นที่ส่วนภาพในการระบุโรคออกจากพื้นที่ส่วนหลัง และการแยกระดับโรคของแต่ละภาพ ผลการทดลองได้ผลลัพธ์ที่น่าเชื่อถือด้วยความแม่นยำโดยเฉลี่ยมากกว่า 80% ในการแยกระดับของโรคในทุกระดับ
การเผยแพร่ผลงาน:
• W. Kusakunniran, Q. Wu, P. Ritthipravat, J. Zhang, Hard Exudates Segmentation based on Learned Initial Seeds and Iterative Graph Cut, Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine (CMPB), 158: 173-183, May 2018, DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.02.011
• W. Kusakunniran, S. Kanchanapreechakorn, K. Thongkanchorn, Instance-based Learning for Blood Vessel Segmentation in Retinal Image, pages 111 – 118, Thailand, July 2019, International Conference on Computing and Information Technology (IC2IT), Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Springer Nature Switzerland (IC2IT 2019, AISC 936), DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-19861-9_11
• R. Kasantikul, W. Kusakunniran, Improving Supervised Microaneurysm Segmentation using Autoencoder-Regularized Neural Network, pages 553 – 559, Australia, December 2018, Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA)
• W. Kusakunniran, Q. Wu, P. Ritthipravat, J. Zhang, Three-Stages Hard Exudates Segmentation in Retinal Images, pages 1 – 6, Thailand, October 2017, International Conference on Information Technology and Electrical Engineering (ICITEE)
รางวัลที่ได้รับ:
• ทุนพัฒนาศักยภาพในการทํางานวิจัยของอาจารย์รุ่นใหม่ สนับสนุนโดยสำนักงานกองทุนสนับสนุนการวิจัย
การติดต่อ:
ผศ. ดร.วรพันธ์ คู่สกุลนิรันดร์
คณะเทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศและการสื่อสาร มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล
Automatic Detection of Diabetes Retinopathy based on Digital Retinal Images
Faculty of Information and Communication Technology, Mahidol University
Project Title:
Detection of Diabetes Retinopathy using Image Processing
Research Title:
Automatic Detection of Diabetes Retinopathy based on Digital Retinal Images
Researcher:
Asst.Prof. Dr.Worapan Kusakunniran
This research project mainly aims to develop novel approaches and computer programs to detect and classify stages of the diabetic retinopathy in retinal images, in an automatic way. This could help filtering patients who may be in the early stage who have a higher chance to be completely treated, or in the urgent needs of the treatments. It could also help giving the service of diabetic retinopathy check-up for people who stay a distance from the medical service. This research project developed the new image processing based methods to segment key visual signals of the diabetic retinopathy such as microaneurysms, hard exudates, and abnormal blood vessels. Such signals were further used in the classification learning processes for classifying the stage of the disease. The deep learning was also attempted to apply on raw retinal images directly for the stage classification. The developed approaches and computer programs were validated with the retinal images in both perspectives of segmentations and classifications. The experimental results illustrated the promising performances of the proposed method with over 80% accuracy of the stage classification in average.


Publishing:
• W. Kusakunniran, Q. Wu, P. Ritthipravat, J. Zhang, Hard Exudates Segmentation based on Learned Initial Seeds and Iterative Graph Cut, Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine (CMPB), 158: 173-183, May 2018, DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.02.011
• W. Kusakunniran, S. Kanchanapreechakorn, K. Thongkanchorn, Instance-based Learning for Blood Vessel Segmentation in Retinal Image, pages 111 – 118, Thailand, July 2019, International Conference on Computing and Information Technology (IC2IT), Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Springer Nature Switzerland (IC2IT 2019, AISC 936), DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-19861-9_11
• R. Kasantikul, W. Kusakunniran, Improving Supervised Microaneurysm Segmentation using Autoencoder-Regularized Neural Network, pages 553 – 559, Australia, December 2018, Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA)
• W. Kusakunniran, Q. Wu, P. Ritthipravat, J. Zhang, Three-Stages Hard Exudates Segmentation in Retinal Images, pages 1 – 6, Thailand, October 2017, International Conference on Information Technology and Electrical Engineering (ICITEE)
Award Grant related to the Project:
• Research Grant for New Scholar, supported by Thailand Research Fund
Key Contact Person:
Asst.Prof. Dr.Worapan Kusakunniran
Faculty of Information and Communication Technology, Mahidol University