Study of Design and Development for Logistics Infrastructure and Integrated Information System and Guidelines of Healthcare Big Data for Thailand Digital Economy Phase II
ศูนย์การจัดการโลจิสติกส์และโซ่อุปทานสุขภาพ คณะวิศวกรรมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล


{:th}
Study of Design and Development for Logistics Infrastructure and Integrated Information System and Guidelines of Healthcare Big Data for Thailand Digital Economy Phase II
ศูนย์การจัดการโลจิสติกส์และโซ่อุปทานสุขภาพ คณะวิศวกรรมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล
ผลงานวิจัย :
Study of Design and Development for Logistics Infrastructure and Integrated Information System and Guidelines of Healthcare Big Data for Thailand Digital Economy Phase II
ผู้วิจัย :
รศ.ดร.ดวงพรรณ ศฤงคารินทร์ และคณะ
Thailand Health expenditure has increased rapidly every year. In 2016, the expenditure increased to 381,387.4 million baht. In this expenditure, drugs contribute almost 40% or 162,917 million baht (NESDB, 2016). Significantly, there is a hidden logistics cost of 14.2% which accounts for 23,134.2 million baht (NESDB, 2016). This logistics cost is composed of Inventory cost 5.4%, transportation cost 7.5% and administration cost 1.3%. The significant root causes for this high logistics cost are lack of information sharing and various data standard with fragmented database. The integration and interoperability between hospitals, suppliers and government sectors are difficult to achieve. In order to develop this SC integration,
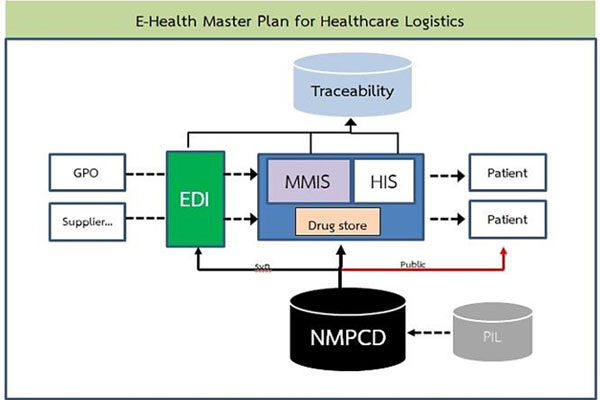
The research team has developed the central database which gathers the data including the drug codes and additional drug information. The National Medicinal Product Catalogue Database: NMPCD collects more than 25,000 codes e.g. 24 – Digit Code / TMT / Reg No. / GTIN / NLEM / UNSPSC. Moreover the research team has designed and developed the Material Management Information System: MMIS, enabling hospitals to efficiently manage drug and medical supply stock. Logistics feature are incorporated to improve hospitals’ logistics performance.

Furthermore Electronic Data Interchange system (EDI) has been designed for data exchange between hospitals and suppliers electronically. Also the traceability system are built to provide tracing and tracking hospital’s drug and medical supply usage. It tracks the drugs from procurement process to dispensing point to patient.
With this systems architecture, interoperability and Supply Chain integration can be achieved. Hospital performance can be improved. Information will be visible throughout the supply chain Drugs can be track and trace all over the country. Big data will be resulted ultimately.
{:}{:en}
Study of Design and Development for Logistics Infrastructure and Integrated Information System and Guidelines of Healthcare Big Data for Thailand Digital Economy Phase II
Centre of Logistics Management and Healthcare Supply Chain (LogHealth), Faculty of Engineering, Mahidol University
Title :
Study of Design and Development for Logistics Infrastructure and Integrated Information System and Guidelines of Healthcare Big Data for Thailand Digital Economy Phase II
Researchers :
Assoc.Prof.Dr.Duangpun Singkarin et al.
Thailand Health expenditure has increased rapidly every year. In 2016, the expenditure increased to 381,387.4 million baht. In this expenditure, drugs contribute almost 40% or 162,917 million baht (NESDB, 2016). Significantly, there is a hidden logistics cost of 14.2% which accounts for 23,134.2 million baht (NESDB, 2016). This logistics cost is composed of Inventory cost 5.4%, transportation cost 7.5% and administration cost 1.3%. The significant root causes for this high logistics cost are lack of information sharing and various data standard with fragmented database. The integration and interoperability between hospitals, suppliers and government sectors are difficult to achieve. In order to develop this SC integration,
The research team has developed the central database which gathers the data including the drug codes and additional drug information. The National Medicinal Product Catalogue Database: NMPCD collects more than 25,000 codes e.g. 24 – Digit Code / TMT / Reg No. / GTIN / NLEM / UNSPSC. Moreover the research team has designed and developed the Material Management Information System: MMIS, enabling hospitals to efficiently manage drug and medical supply stock. Logistics feature are incorporated to improve hospitals’ logistics performance.

Furthermore Electronic Data Interchange system (EDI) has been designed for data exchange between hospitals and suppliers electronically. Also the traceability system are built to provide tracing and tracking hospital’s drug and medical supply usage. It tracks the drugs from procurement process to dispensing point to patient.
With this systems architecture, interoperability and Supply Chain integration can be achieved. Hospital performance can be improved. Information will be visible throughout the supply chain Drugs can be track and trace all over the country. Big data will be resulted ultimately.
Key Contact Person :
Assoc.Prof.Dr.Duangpun Singkarin
Faculty of Engineering, Mahidol University
dungpun.skn@mahidol.ac.th
{:}