ผลของสารปรับปรุงดินต่อการดูดซับแคดเมียมของต้นข้าว
คณะสิ่งแวดล้อมและทรัพยากรศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล



{:th}
ผลของสารปรับปรุงดินต่อการดูดซับแคดเมียมของต้นข้าว
คณะสิ่งแวดล้อมและทรัพยากรศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล
โครงการวิจัย:
ผลของสารปรับปรุงดินต่อการดูดซับแคดเมียมของต้นข้าว
ผู้วิจัย:
ดร.ชิษณุพงศ์ ประทุม
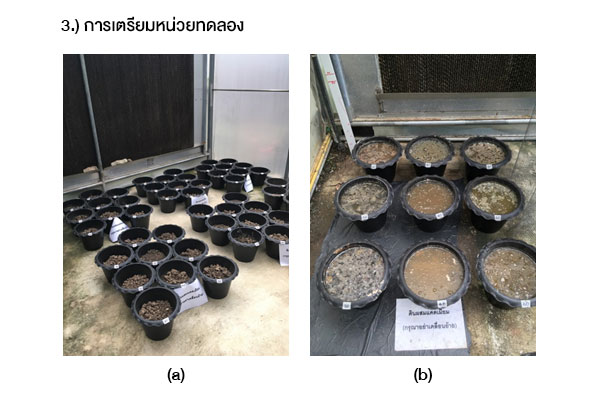
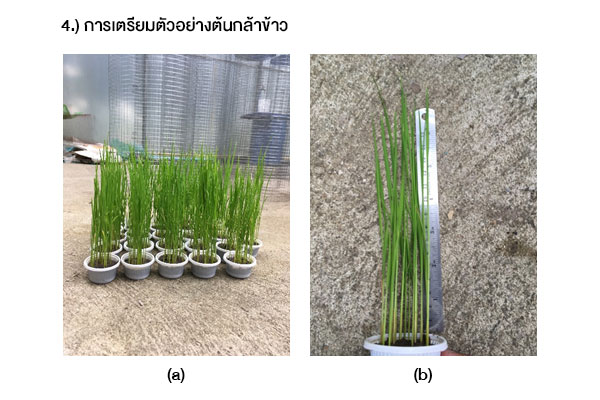
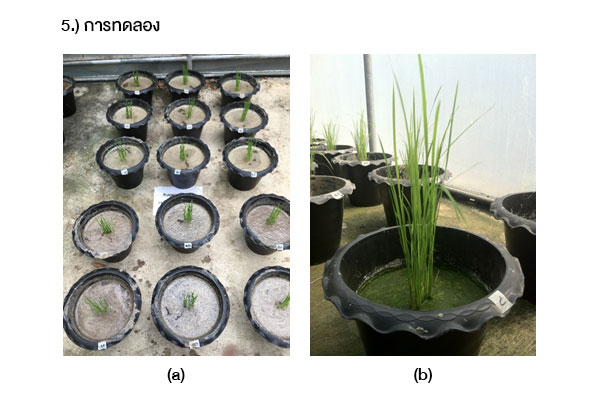
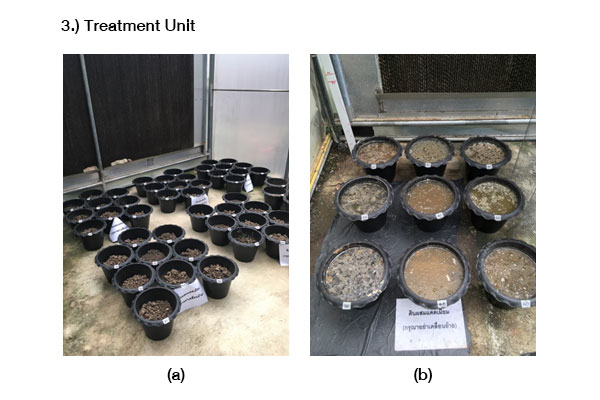
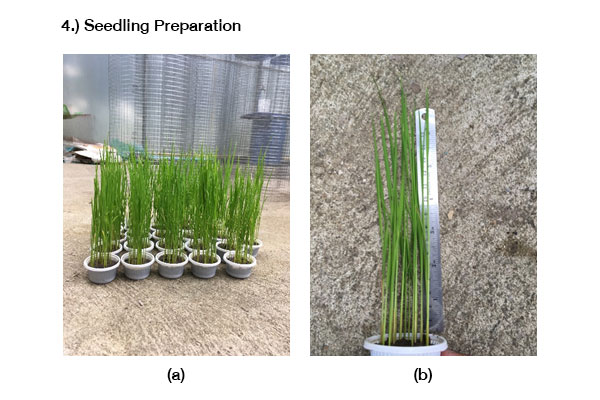
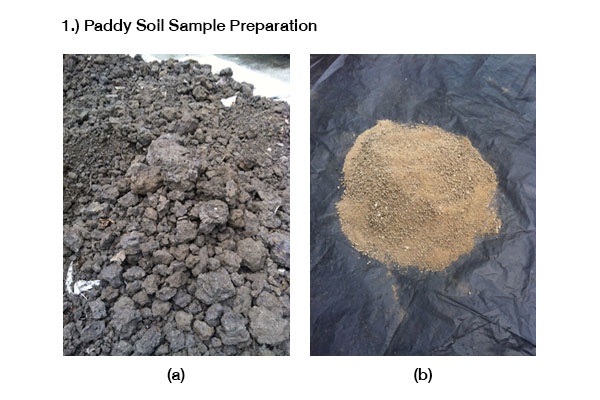
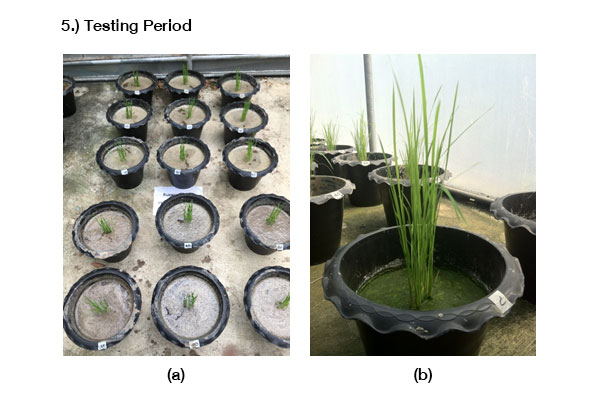
งานวิจัยนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์ เพื่อศึกษาชนิดของสารปรับปรุงดิน ที่มีประสิทธิภาพในการดูดซับแคดเมียมไว้ในดินนา และศึกษาปริมาณแคดเมียมที่มีการสะสมในส่วนต่าง ๆ ของต้นข้าว โดยวางแผนการทดลองแบบสุ่มอย่างสมบูรณ์ จำนวน 3 ซ้ำ ซึ่งใช้ข้าวเจ้าสายพันธุ์สุพรรณบุรี 1 ปลูกในดินนาที่มีการผสมสารปรับปรุงดินร้อยละ 4 ได้แก่ มูลสุกร, มูลโคนม, มูลไก่แกลบ, ปุ๋ยหมัก และมูลไส้เดือน และมีความเข้มข้นของแคดเมียม 3 ระดับ ได้แก่ 20, 40 และ 60 มิลลิกรัม/กิโลกรัม ผลการศึกษา พบว่าที่ความเข้มข้นร้อยละ 4 ของมูลสุกร และมูลโคนม ต้นข้าวไม่สามารถเจริญเติบโต และแห้งตายลง ในวันที่ 70 ของการเพาะปลูก ส่วนมูลไก่แกลบ มีประสิทธิภาพสูงสุดในการดูดซับแคดเมียมไว้ในดินนา ขณะที่ปุ๋ยหมัก สามารถกระตุ้นให้รากของต้นข้าวดูดซึมแคดเมียมในดินนาได้มากขึ้น จึงทำให้ลดการสะสมแคดเมียมไว้ในลำต้น ใบ และโดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งเมล็ดข้าว ทั้งนี้พบการสะสมแคดเมียมในราก > ลำต้น > ใบ > เมล็ดข้าว




การเผยแพร่ผลงาน:
• Chitsanuphong Pratum. 2019. Response of Cadmium Accumulation in Rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. SPR1) Grown with Different Organic Soil Amendments. Pertanika J. Sci. & Technol. 27(1) : 443-458
การติดต่อ:
ดร.ชิษณุพงศ์ ประทุม
คณะสิ่งแวดล้อมและทรัพยากรศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล
08 5295 5339
chitsanuphong.pra@mahidol.ac.th, chitsanuphong.pra@mahidol.edu
The Effect of Soil Amendments on the Uptake of Cadmium by Rice.
Faculty of Environment and Resource Studies, Mahidol University
Project Title:
The Effect of Soil Amendments on the Uptake of Cadmium by Rice.
Researcher:
Dr.Chitsanuphong Pratum
This study aims to determine the type of the effective soil amendments for cadmium absorption in the paddy soil. It also investigated the amount of cadmium accumulation in various parts of the rice plants. The research methodology was performed in Completely Randomized Design (CRD), which three replications. The Suphanburi 1 rice variety and 4% of soil amendments (pig manure, dairy cow manure, poultry manure – rice husk, organic compost, and vermicompost) were used for this study. The cadmium contents in each the paddy soil samples were 20, 40, and 60 mg/kg dry weight, respectively. The results found that the rice plants cannot grow wither and die on the 70th day of cultivation at 4% of dairy cow manure and pig manure. In addition, poultry manure – rice husk was highly effective for cadmium adsorption in the paddy soil. Whereas, organic compost can stimulate the roots of the rice plants to absorb cadmium in soil were more. This reduces the accumulation of cadmium in stems, leaves, and especially rice grain. In part of, the investigation of the amount of cadmium accumulation in various parts of the rice plants found that the cadmium accumulation in roots > stems > leaves > rice grain, respectively.



Publishing:
• Chitsanuphong Pratum. 2019. Response of Cadmium Accumulation in Rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. SPR1) Grown with Different Organic Soil Amendments. Pertanika J. Sci. & Technol. 27(1) : 443-458
Key Contact Person:
Dr.Chitsanuphong Pratum
Faculty of Environment and Resource Studies, Mahidol University
08 5295 5339
chitsanuphong.pra@mahidol.ac.th, chitsanuphong.pra@mahidol.edu