การตอบสนองทางสรีรวิทยาแบบเฉียบพลันขณะออกกำลังกายท่าทางต่าง ๆ ในหญิงตั้งครรภ์
วิทยาลัยวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยีการกีฬา มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล

{:th}
การตอบสนองทางสรีรวิทยาแบบเฉียบพลันขณะออกกำลังกายท่าทางต่าง ๆ ในหญิงตั้งครรภ์
วิทยาลัยวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยีการกีฬา มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล
ผลงานวิจัย :
การตอบสนองทางสรีรวิทยาแบบเฉียบพลันขณะออกกำลังกายท่าทางต่าง ๆ ในหญิงตั้งครรภ์
ผู้วิจัย :
รุ่งชัย ชวนไชยะกูล
เมตตา ปิ่นทอง
อมรพันธ์ อัจจิมาพร
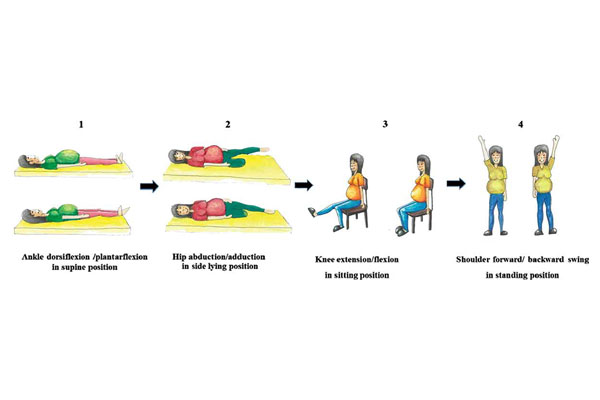
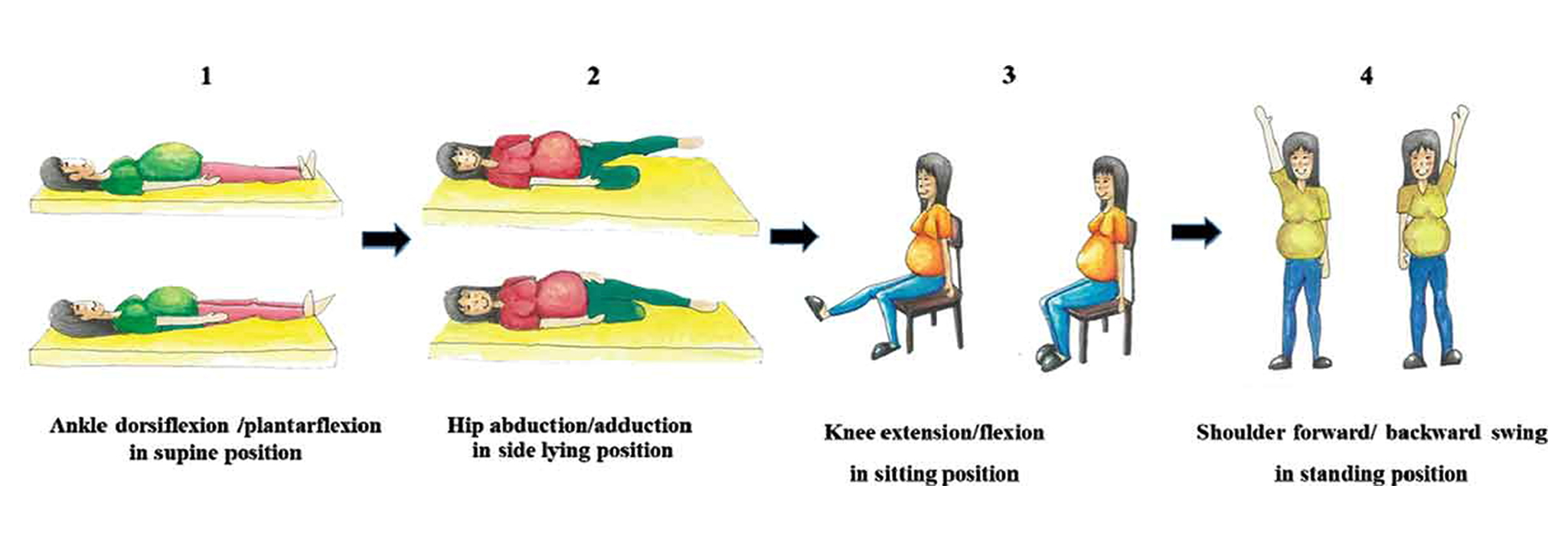
วัตถุประสงค์ : เพื่อวัดการตอบสนองทางสรีรวิทยาของร่างกายที่เกิดขึ้นแบบทันทีทันใด (เฉียบพลัน) ในหญิงตั้งครรภ์ ขณะออกกำลังกายในท่านอนหงาย นอนตะแคง นั่ง และยืน
วิธีวิจัย : เป็นการศึกษาแบบตัดขวาง (Cross – Sectional Study) ในหญิงตั้งครรภ์สุขภาพดี จำนวน 42 คน โดยทำการแบ่งเป็น 3 กลุ่ม ๆ ละ 14 คน ตามระยะเวลาตั้งครรภ์ คือ ไตรมาสที่ 1 2 และ 3 ตามลำดับ ค่าตัวแปรเริ่มต้นจะถูกวัดในท่านั่งพัก เป็นเวลา 30 นาที จากนั้นค่าต่าง ๆ จะถูกวัดขณะที่มีการออกกำลังกายแบบไม่ใช้แรงต้าน ในท่านอนหงาย นอนตะแคง นั่ง และยืน ตามลำดับ ตัวแปรทางสรีรวิทยาที่วัด ประกอบด้วย อัตราการเต้นของหัวใจ (HR) ปริมาณอากาศที่หายใจเข้าออกต่อหนึ่งนาที (VE) อัตราการใช้ก๊าซออกซิเจน (VO2) อัตราการผลิตก๊าซคาร์บอนไดออกไซด์ (VCO2) และค่าอัตราส่วนระหว่างอัตราการใช้ออกซิเจน และอัตราการเต้นของหัวใจ (VO2/HR) โดยตัวแปรจะถูกวัดด้วยเครื่องวัดอัตราการใช้พลังงานแบบอ้อม
ผลการวิจัย : เมื่อเปรียบเทียบกับค่าเริ่มต้น พบว่าหญิงตั้งครรภ์ทุกไตรมาสมีค่า HR, VE, VO2 และ VCO2 เพิ่มขึ้นขณะออกกำลังกายในท่ายืน ค่า VO2 มีค่าเพิ่มขึ้นในขณะออกกำลังกายในท่านั่ง และค่า VO2/HR มีค่าเพิ่มขึ้นในทุก ๆ ท่าของการออกกำลังกาย ยกเว้น ท่ายืน นอกจากนี้ยังพบอีกว่าหญิงตั้งครรภ์กลุ่มไตรมาส 2 และ 3 มีค่า HR ลดลงอย่างมีนัยสำคัญในขณะออกกำลังกายในท่านอนหงาย
สรุปผล : การศึกษานี้ชี้ให้เห็นว่า การตอบสนองทางสรีรวิทยาแบบเฉียบพลันมีรูปแบบที่คล้ายกัน ในขณะออกกำลังกายด้วยท่าทางต่าง ๆ ในทุก ๆ ไตรมาสของหญิงตั้งครรภ์ ยิ่งกว่านั้น การออกกำลังกายในท่ายืน จะส่งผลให้เกิดการเปลี่ยนแปลงทางสรีรวิทยาที่กระทำต่อการทำงานของระบบหัวใจและหายใจมากกว่าการออกกำลังกายท่านอนหงาย นอนตะแคง และท่านั่ง
การนำไปใช้ประโยชน์ : ให้ความรู้แก่บุคลากรทางแพทย์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการดูแลหญิงตั้งครรภ์ในโรงพยาบาลต่าง ๆ เช่น โรงพยาบาลรามาธิบดี โรงพยาบาลธรรมศาสตร์เฉลิมพระเกียรติ โรงพยาบาลพระมงกุฎเกล้า
การเผยแพร่ผลงาน : Physiotherapy Theory and Practice, 18 มีนาคม 2018, หน้า 1 – 7
การติดต่อ :
ผศ.ดร.อมรพันธ์ อัจจิมาพร
วิทยาลัยวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยีการกีฬา มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล
g4036011@gmail.com
{:}{:en}
Acute Physiological Responses in Pregnant Women during Exercises in Different Positions
College of Sports Science and Technology, Mahidol University
Title :
Acute Physiological Responses in Pregnant Women during Exercises in Different Positions
Researchers :
Rungchai Chaunchaiyakul
Metta Pinthong
Amornpan Ajjimaporn
Objective : This study measured acute physiological responses in pregnant women during short duration exercise in the supine (Sup), side-lying (Side), sitting (Sit), and standing (Std) positions.
Methods : In a cross-sectional study, 42 healthy pregnant women were divided into 3 groups of 14 persons each: G1, G2, and G3 (first, second, and third trimester, respectively). Baseline assessments were performed following a 30-min rest in the sitting position. Subsequent measurements were then obtained while exercising, without resistance, in the Sup, Side, Sit, and Std, respectively. Physiological parameters, including heart rate (HR), minute ventilation (VE), oxygen consumption (VO2), carbon dioxide production (VCO2), and oxygen pulse (VO2/HR), were collected using the indirect calorimetry.
Results : Comparing resting values, all groups had a significantly increased (1) HR, VE, and VCO2 during the Std, (2) VO2 values during the Sit and Std, and (3) O2 pulse values during short duration exercise in all positions except the Std, whereas only G2 and G3 had a significantly decreased HR during the Sup.
Conclusion : This study points that acute physiological responses to the positional challenge similarly occur in all trimester of pregnant women. Short duration exercise in the Std positions exerts more physiologic stresses on cardiorespiratory functions than in the Sup, Side, and Sit positions.
Applied Research Project to Usage : To provide knowledge to provider health professional (Physician, Nurse) at Ramathibodi Hospital, Phramongkutklao Hospital, Thammasat University Hospital

Publishing : Physiotherapy Theory and Practice, 18 March 2018, Pages 1 – 7
Key Contact Person :
Asst.Prof.Dr.Amornpan Ajjimaporn
College of Sports Science and Technology, Mahidol University
g4036011@gmail.com
{:}