Mahidol University Salaya Master Plan 2008
Fundamental Concept of Mahidol University Toward Greens University
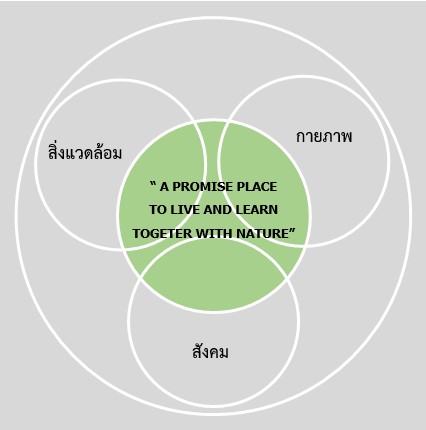
Mahidol University Salaya’s University Master Plan 2008 proposes to improve Mahidol University Salaya into a “Dream City University.” This is envisioned as having a learning environment that is conducive to learning, and is geographically and physically located in harmony with its environment and culture. As a second home for all Mahidol people, Mahidol University is also a spiritual center. All physical, social, and environmental factors go into creating “A Promised Place to Live and Learn Together with Nature”:
- A social aspect is establishing a learning community;
- A physical aspect is creating a comfortable, conducive environment for living and studying; and
- The environment refers to a holistic environment that includes both natural and creative environments, as well as the community outside the university.
Green University’s vision is to build a university that promotes learning through nature. The arboretum at the heart of Green University is its primary focus. This helps accelerate Mahidol University to integrate a green environment (shady environment), promote health, cleanliness, pollution-free, and realize the valuable use of resources. The university provides beautiful landscapes designed to be harmonious with nature. There are open spaces and green areas for recreation and conducive to learning activities of nature and the environment. It encourages the consumption of energy and encourages the use of renewable energy in order for students and the Mahidol community to be able to live happily on the Salaya Campus of Mahidol University, resulting in high quality of life and going green. It also aims to make Mahidol University Salaya Campus be a leader in neighboring communities in terms of environmental protection and coexistence with nature.
The 3 Greens strategy in developing a Green University
- Greens 1 Safe and Healthy Campus; enhancing quality of by providing a good and safe working environment
– There is a wide variety of plants including local flora, medicinal plants and plants for research studies.
– Increase the number of trees in the university especially around the activity area and various walkways.
– Design unique gardens and landscapes that fit with historical, cultural, and architectural contexts of Mahidol University
– Using technologies such as wastewater treatment systems, gray water irrigation, recycling waste and reducing air pollution without encouraging the use of cars, or burning garbage is a way to reduce pollution and pollution from cars. Using bicycles instead of cars is a method of reducing air pollution.
- Greens 2 Green Education & Technology; supports teaching, research, development and technology transfer leading to a sustainable green university
– Add courses and electives in sustainable development, environmental conservation, and academic services and continuing education in environmental conservation.
– The emphasis of the program is on science research, conservation, restoration, and enhancement of the quality of the environment.
– Develop innovative technologies and processes to create environmentally friendly products.
– The development of scientific and technological knowledge for protecting the environment around Mahidol University and within the surrounding community
- Greens 3 Green Preservation Energy; a well-managed university will take advantage of cost-effective, energy-efficient resources for maximum effect.
– The design of energy-saving structures uses natural light and reduces the outside temperature.
– Increase walking, cycling, and public transportation to reduce energy consumption from oil and move to electric or renewable vehicles.
– Add different types of renewable energy alternatives both for transportation and for daily use.
– In order to reduce electricity consumption, management can turn off lights during the day to save energy, and turn down air conditioning and use electrical appliances sparingly.
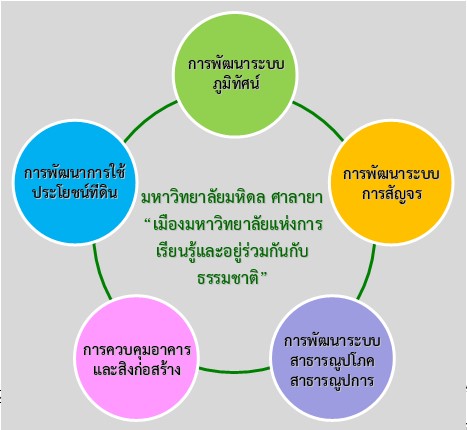
The development guidelines for the university, according to the 2008 master plan consist of 5 areas of development: land use development; development of landscape systems, mobility system development, public utility system development, and building and construction control.
- Land use development
To ensure continuity and the formation of gatherings of the same activities. Moreover, to control the growth of various activities and conserve the good environment and nature as important resources of the university.
1.1 Concept
1) Activities of the same type will be grouping in the same or contiguous area as much as possible for the right proportion and to connectedness in both terms of environmental quality and safety.
2) The density of land use in future will be increased sufficiently and appropriately by maintaining the vacant area of at least 70 percent of the total area.
3) A sub-block system will be introduced to divide the space in each activity area.
4) Green area and important spaces will be selected for the University and the Mahidol community.
1.2 Types of land use
Zone 1 Land Use for Education
Block 1/1 Main Study Area
Block 1/2 Educational Area for Arts and Culture
Block 1/3 Health Educational Area
Zone 2 Land Use for Administrative and Central Services
Block 2/1 Mahidol Learning Center and Chao Fa Park
Block 2/2 Mahidol Sitthakan Area
Zone 3 Land use for Research and Academic Services
Block 3/1 Main Research Center Area
Block 3/2 Academic Service Area
Block 3/3 Research Center Area
Block 3/4 Area on the Southside of Borommaratchachonnani Road
Zone 4 Residential Land Use
Block 4/1 Student Residential Area
Block 4/2 Residential area of Students, Instructors, and Staff (Condominiums)
Zone 5 Land Use for Sports and Recreation
Block 5/1 Sports Center Area
Block 5/2 Outdoor Sports and Recreation Area 1
Block 5/3 Outdoor Sports and Recreation Area 2
Zone 6 Land use for Public Utilities
Block 6/1 Wastewater Treatment Plant
Block 6/2 Area of Environmental Conservation Building and Organic Fertilizer Production Plant
Block 6/3 Substation Area
Zone 7 Area used by other govenmnet agencies (Mahidol Wittayanusorn School)
Zone 8 Land Use for Commercialization
Block 8/1 Area for Large Project Development
Block 8/2 MU Corner Area
Zone 9 Land Use for Environmental Conservation
Block 9/1 Siri Rukkhachat Natural Park
Block 9/2 Southeast Green Area
Block 9/3 Northeastern Green Area
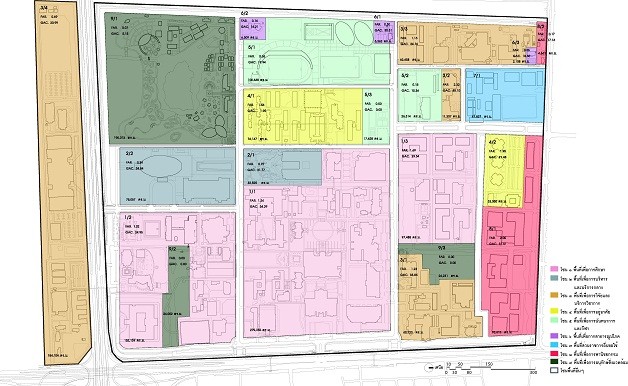
Land Use Plan
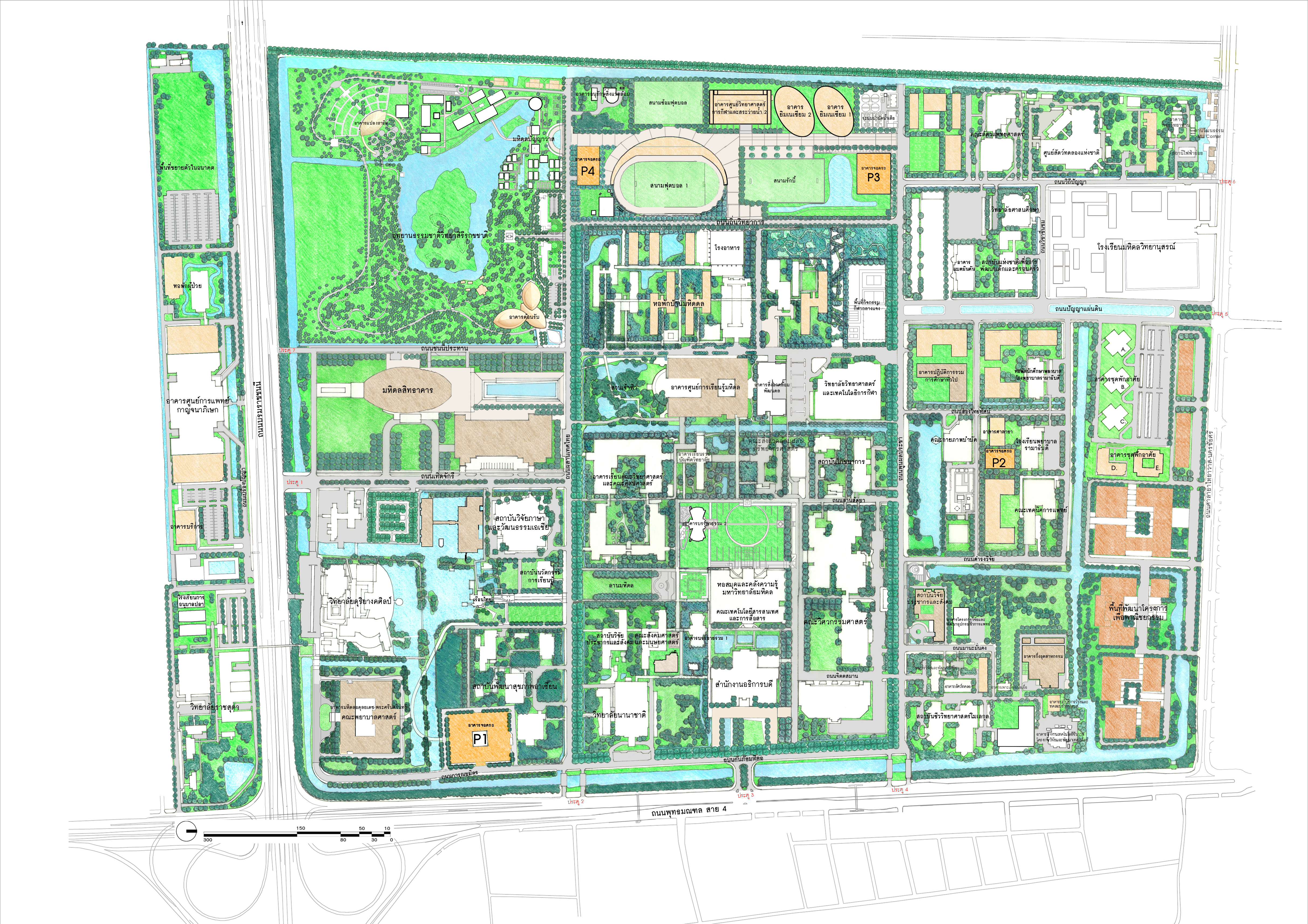
Master Plan Mahidol University Salaya Campus Master Plan 2008 edition
-
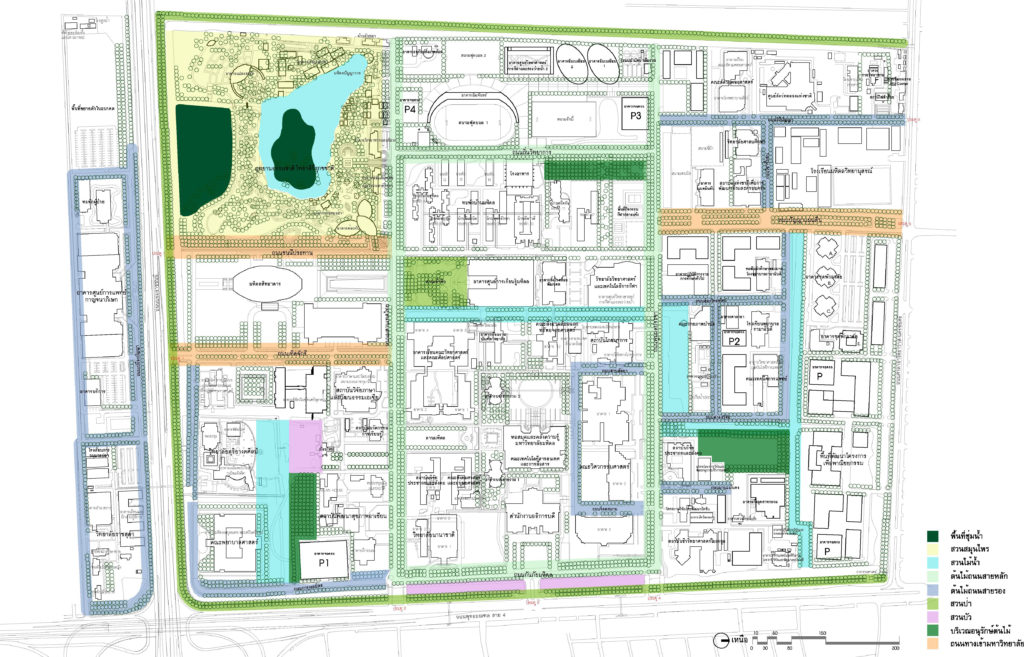
- Development of Landscape Systems
2.1 Concepts
The baseline is to create a landscape and environment that is shady and peaceful and to promote a learning community atmosphere. The three key concepts can be pointed out as follows:
Firstly, the university aims to preserve green spaces rich in plant species and to maintain each area’s ecosystem as near as possible to its natural state.
Secondly, the university aims to create open, green spaces for sports, recreational, and educational activities, as well as building and structure elements that are balanced.
Lastly, the university aims to establish a “Green Way” (เป็นทำที่ใช้ในเอกสารต้นฉบับ) that connect all facilities, in order to present the university as a place where learning is conducted and habitats are created in a natural environment.
2.2 Development of Landscape System within Mahidol University Salaya consists of
2.2.1 The University Axis consists of
1) East-West Green Axis is the main road for walking and cycling within the study area, which connects from Gate 3 to the road in front of the student dormitory and sports center area.
2) North-South Green Axis is the main road for walking and cycling starting from the entrance and the road beside Mahidol Sitthakan separated from Borommaratchachonnani Road connecting to Wittaya Road to Salaya Thai Yawat-Nakhon Chaisri Road
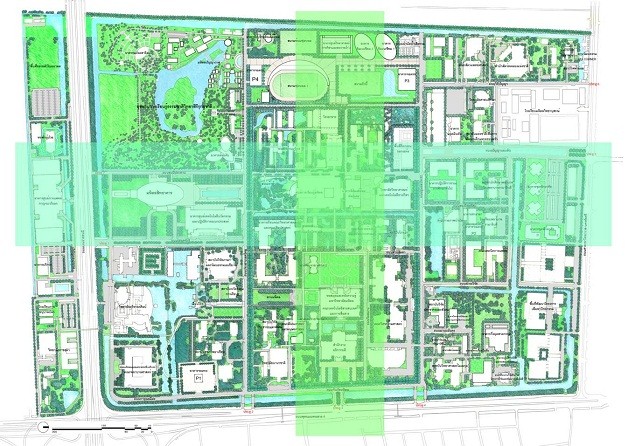
The layout shows the main green axis of the university.
2.2.2 Vista, Landmark & Visual Corridor are to create a beautiful physical image of a memorable and unique university, which builds awareness of directions and pathways as well as creating a shady scenery.
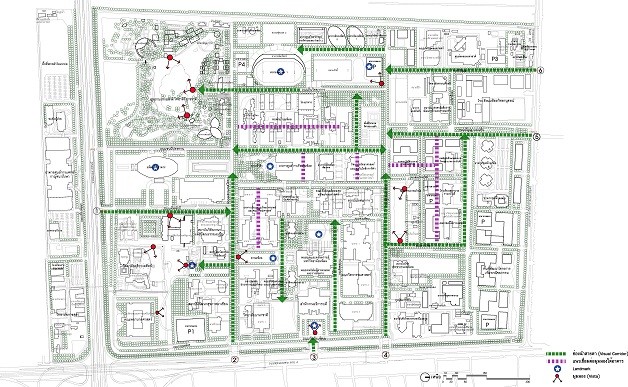
A diagram showing Vista, Landmark & Visual Corridor
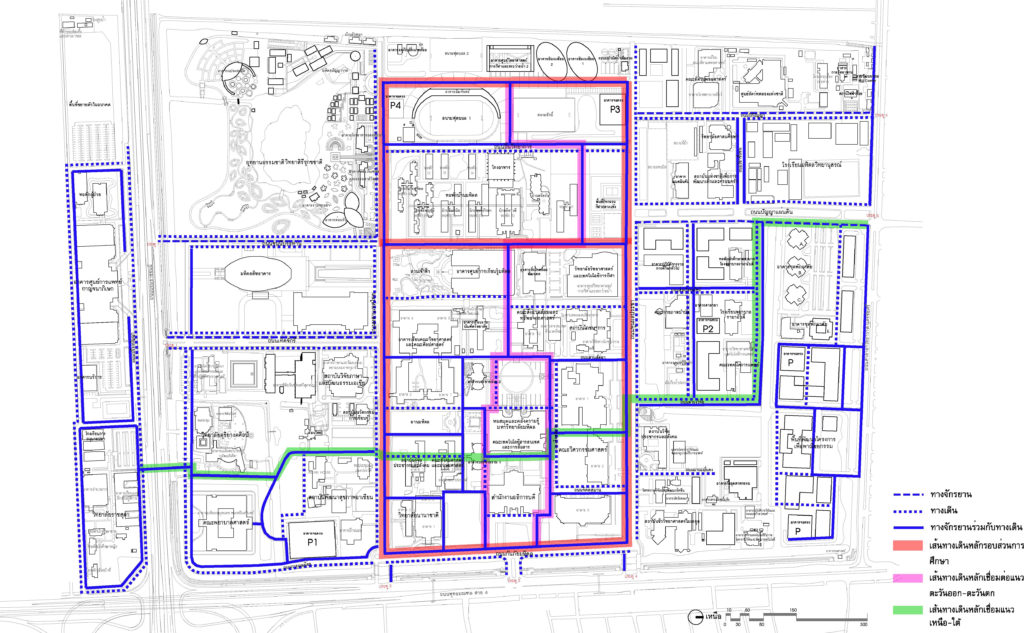
2.2.3 Social Activity Node & Facility Node is designed to be an area outside the building to support various activities and to encourage the university to have more opportunities to meet and socialize. The area is being divided into three sections which are activities area, walkway area, and service point.
2.2.4 Green Network is to connect various types of park areas by connecting green areas through “Green Circulation” in a form of a garden path resulting in a large continuous green area
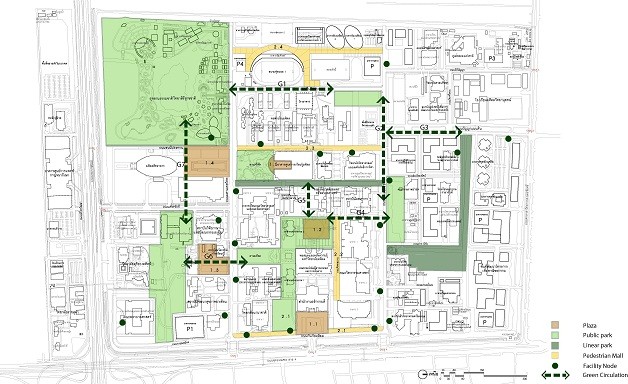
The plan shows the activity area and the green area network.
2.2.5 Sports and Recreation Area Systems have been categorized into four (4) categories of sports and activity areas: the main stadium area, the lawn area for exercise, the swimming pool for paddling, and the bicycle paths for relaxation and exercise.
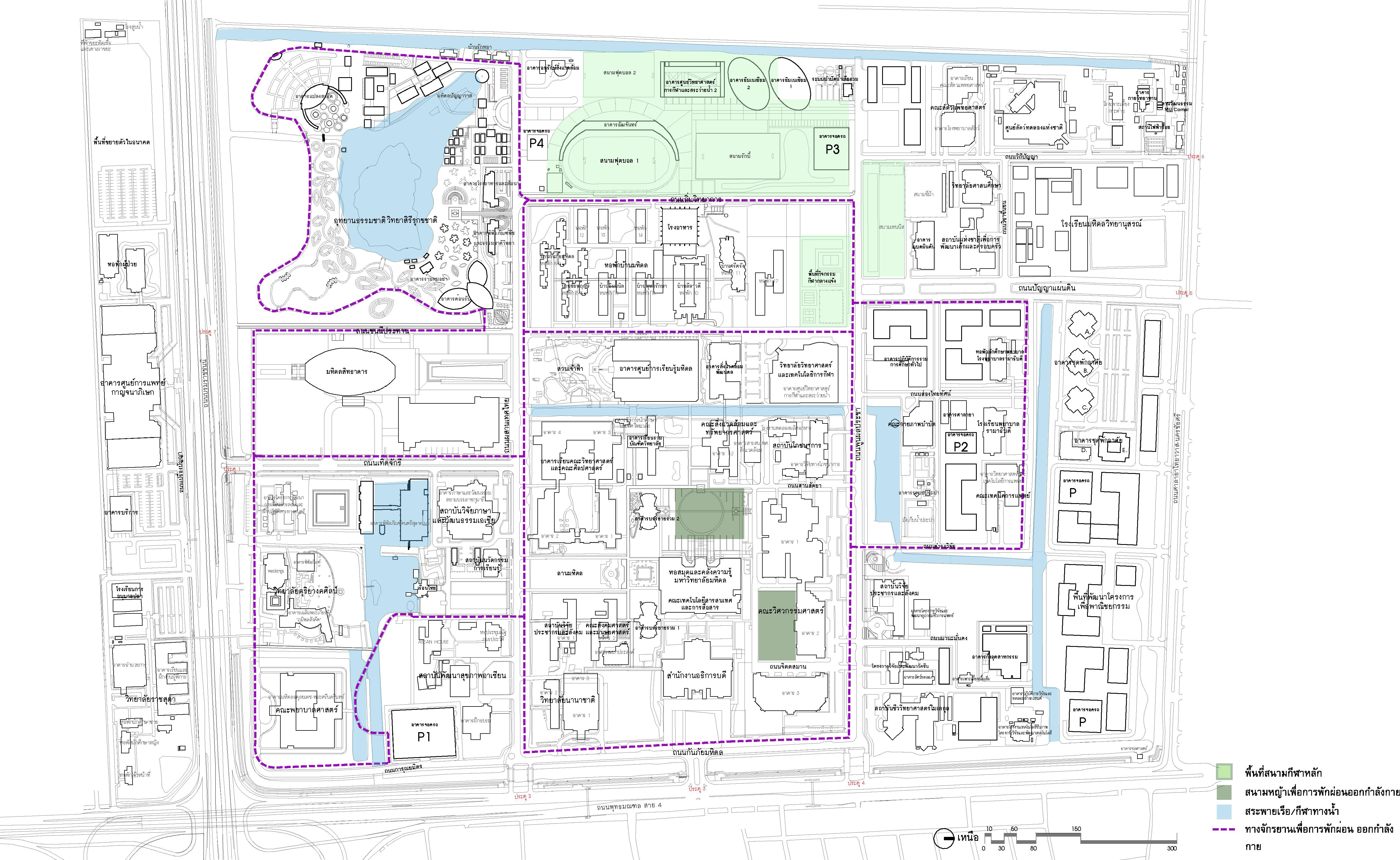
Plan showing areas for sports and recreation
2.2.6 Planting Use System is taking into account the ecosystem of living things at the tree canopy level by connecting ecosystems both the existing and the newly created ecosystems to be green and natural together with the concept of Tree Canopy Landscape Ecology by considering the size of the three tree sizes: perennials, shrubs, and ground cover.

Concept showing of Tree Canopy Landscape Ecology
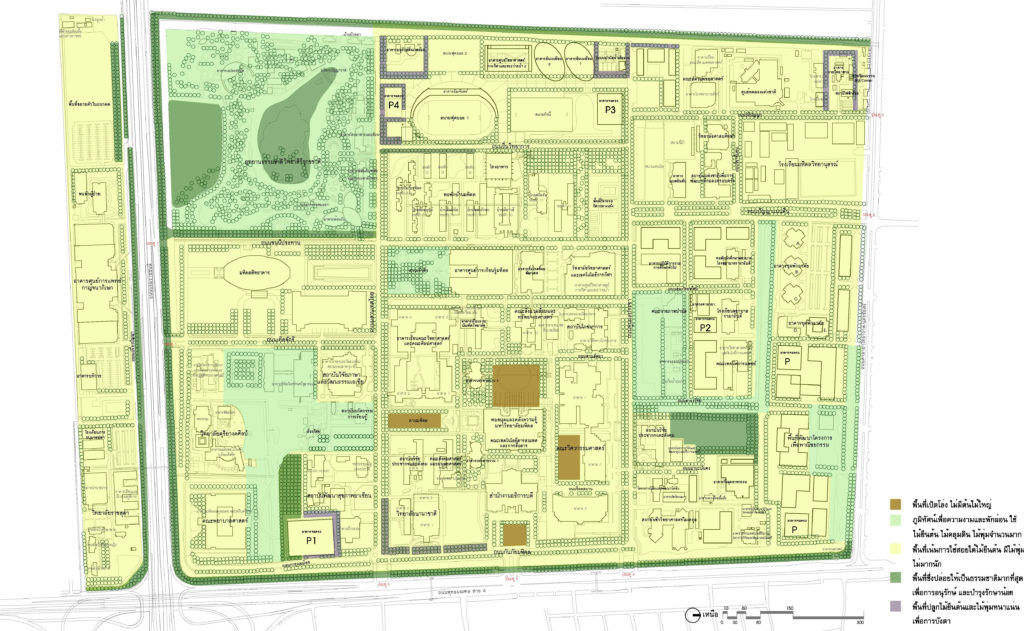
Diagram showing the Planting System
2.2.7 Landscapes Planting Concept select plants for different types of areas based on two important concepts, which are the selection of plants classified according to the importance of each road and selection of plants according to the topography of the garden area.
Plan showing green area and plant selection concept.
2.2.8 Lighting Concept takes into account various types of garden design concepts, as well as the area used at night. More importantly, the design guidelines are made to meet pleasantness and functionality. This is consistent with the use of the brightness of the area by the character of each location which the master plan has determined the appropriate brightness based on the landscape architectural design standards.
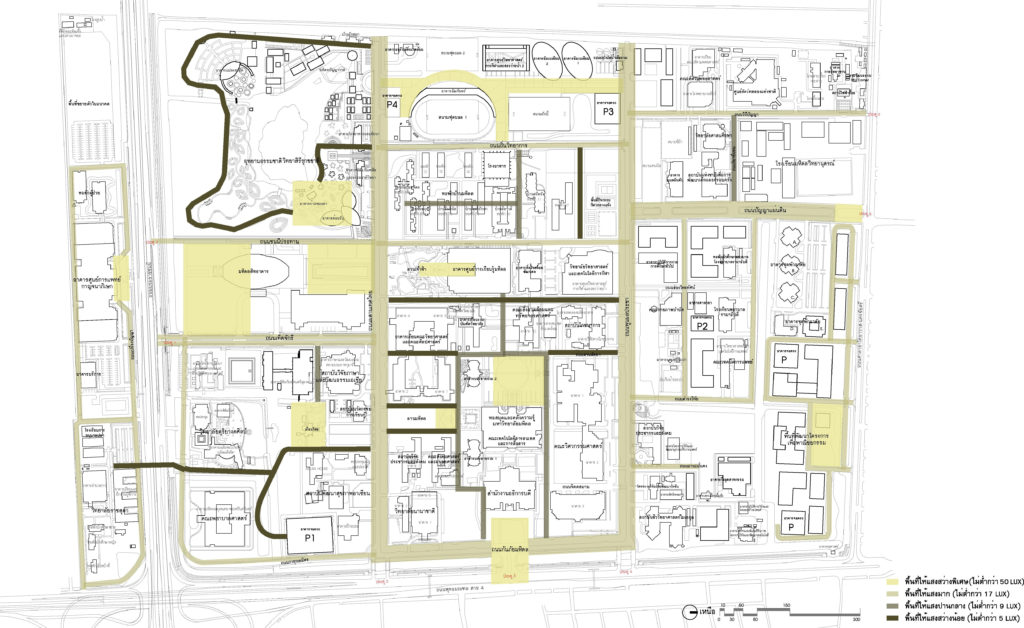
Layout showing the lighting system in the landscape.
-
- Development of the Traffic System
3.1 Concept
By focusing on the development of road, parking systems, bike path, and pedestrian systems in accordance with the Green University, consisting of safety, tidiness, environmentally sustainability, and community satisfaction the development concepts are specified as follows:
1) To reduce the importance of driving, universities were converted to encourage walking and bicycling. By turning the original road surface into a bicycle and pedestrian lane with a shady landscape, the road was reduced to only three lanes with no central island.
2) Providing adequate traffic routes to cover the newly developed areas as necessary.
3) Controlling the car traffic route in the area outside the educational building group to keep the area within the study area for walking and cycling to ensure safety, under shade, and close to nature.
4) Construction of parking structure and converting the original parking area to be a green space to accommodate the activities of students and personnel.
5) Focusing on public transport services and the university’s transportation by walking and cycling.
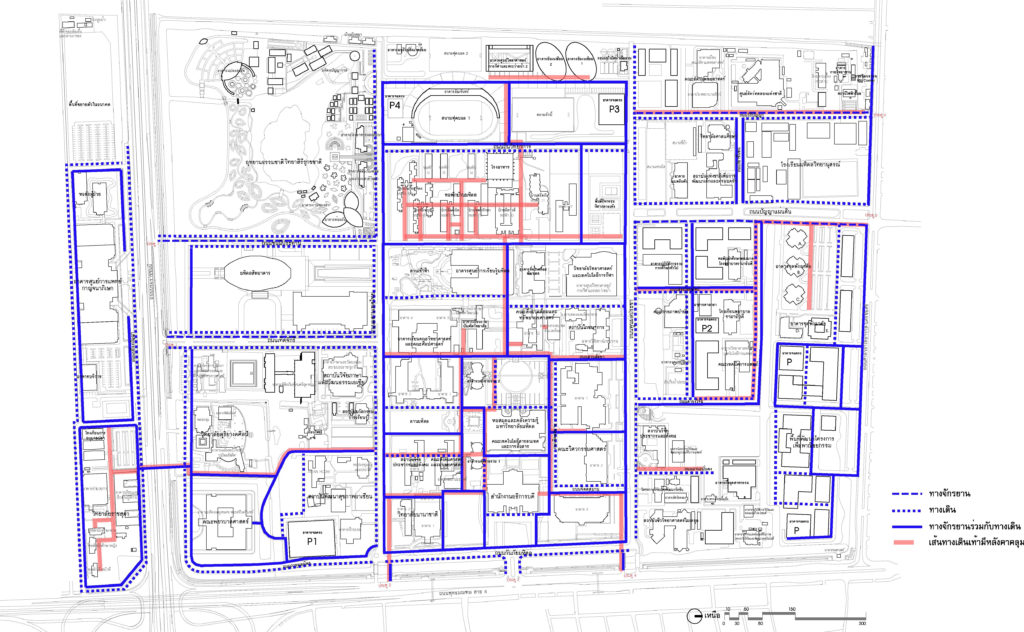
3.2 Road System and Car Parking
3.2.1 Transport network routes classified as
– 7 main roads act as a thoroughfare in-out and main routes for traveling to different areas on campus
– 10 secondary roads serve as roads connecting the main roads to the areas within the various departments.
– Service roads and thoroughfares within the university
– Walking street and service only during the period (time interval)
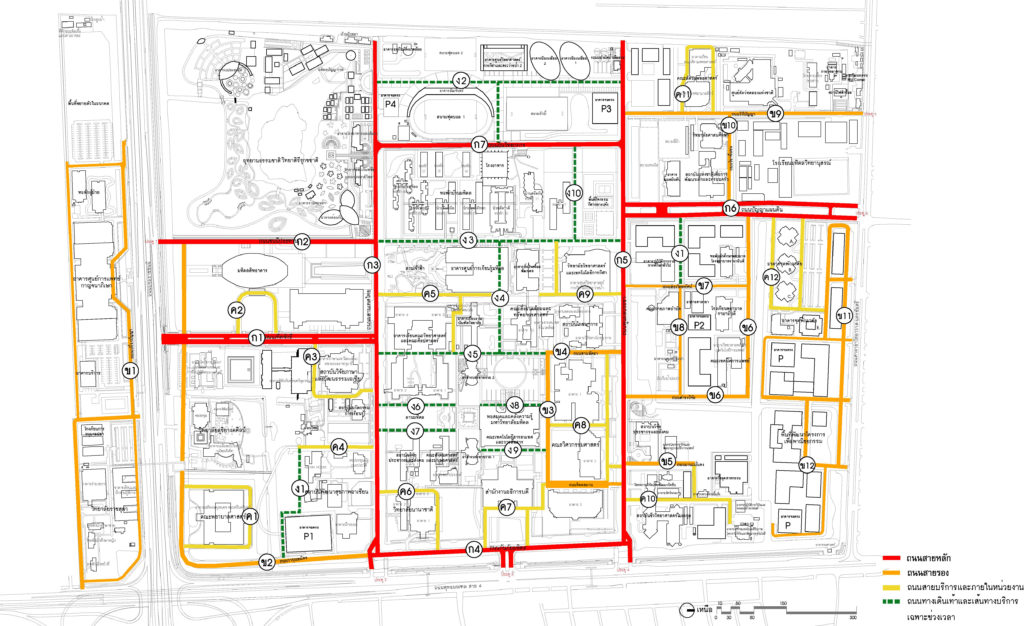
Layout showing the main road – secondary roads
3.2.2 Access and traffic direction, which specified 7 entrances and exits to the university
3.2.3 Parking system and car parking are proposed to construct 4 parking buildings to accommodate approximately 2,000 cars in the future, along with the development of a mass transit system to transport people to a different location. While the parking structure is not yet completed, a temporary parking lot will be built.
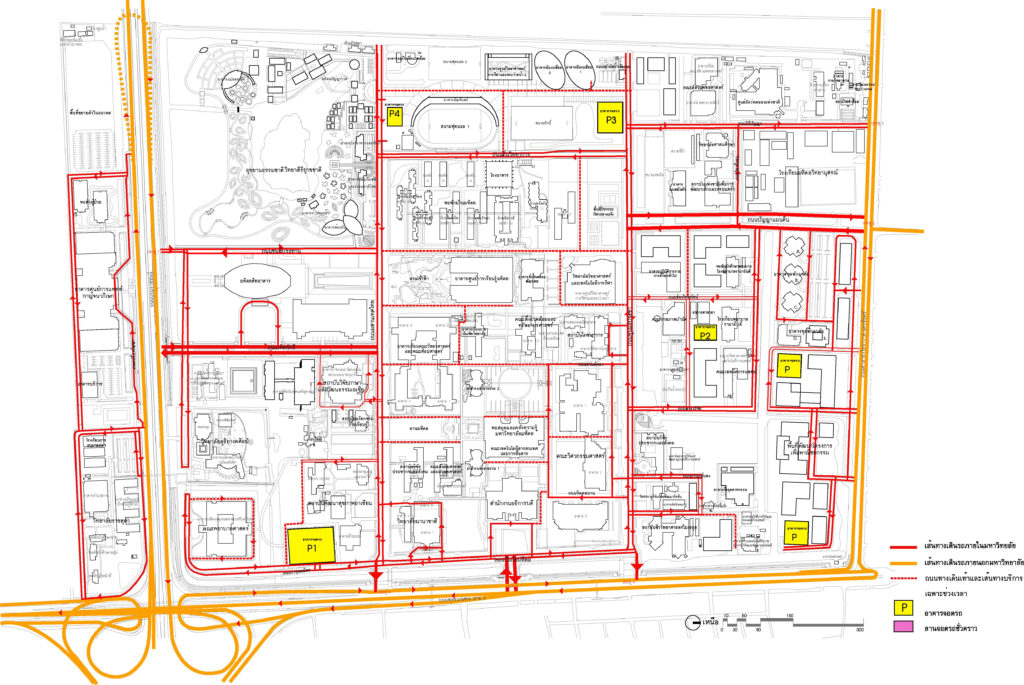
Plans showing roads, car routes, and parking lots
3.3 Bicycle Path System and Bicycle Parking
It consists of a main and a secondary bike path parallel to the walkway by separating channels for safety and shads. This is to encourage the use of bicycles to travel more.
The map showing the bike path
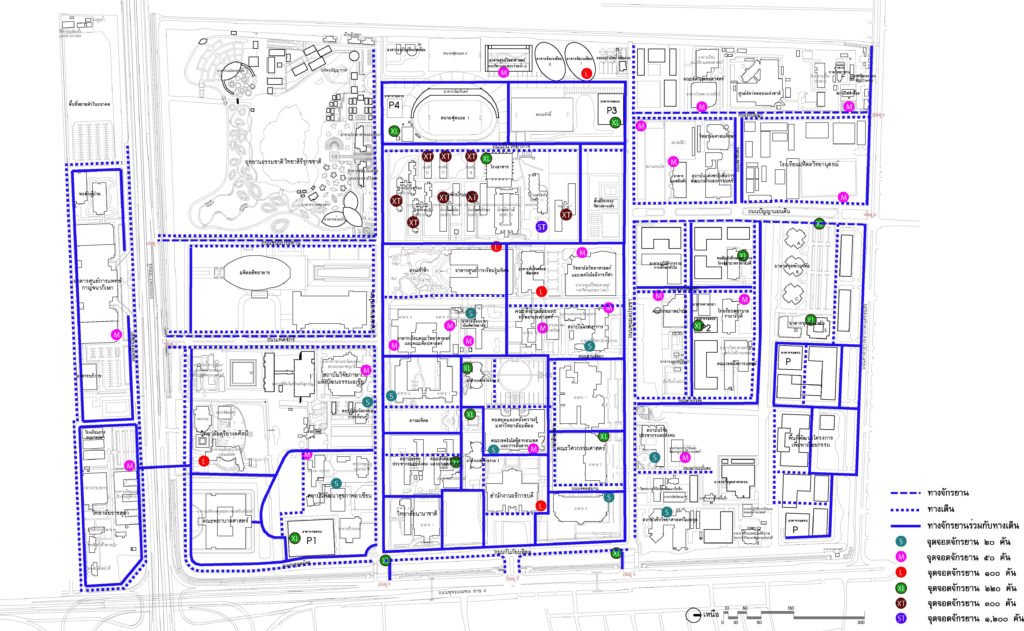
Plans showing bike lanes and bike parking spots
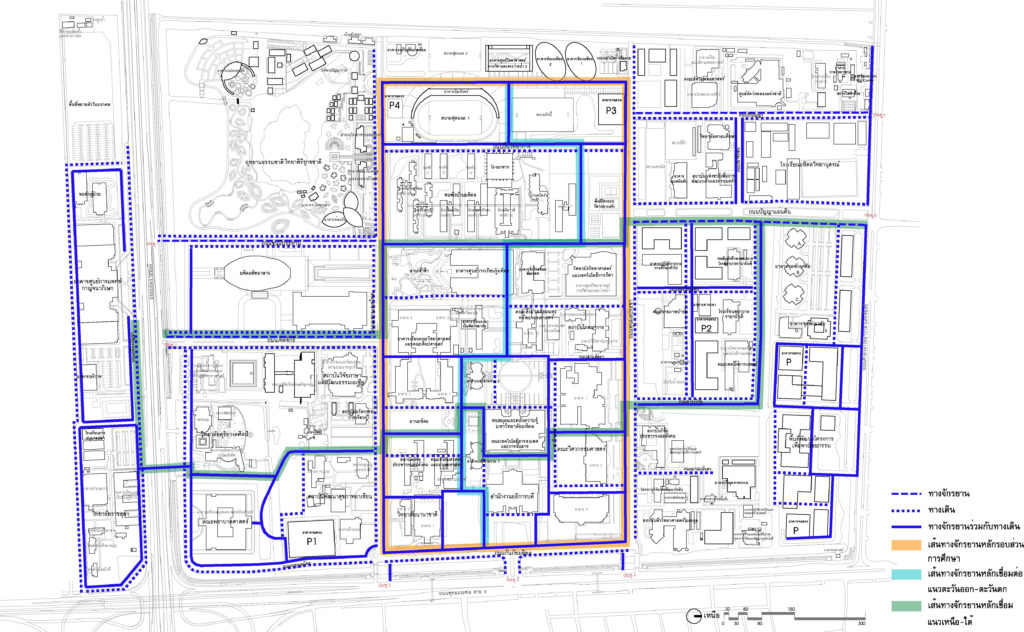
3.4 Pedestrian System
It consists of main and secondary routes. The functional roles of the pavement are defined by its activities and connected with the landscape system, based in the ease of access, safety, and being a part of nature.
Pedestrian schematic
The plan shows a covered pedestrian walkway.
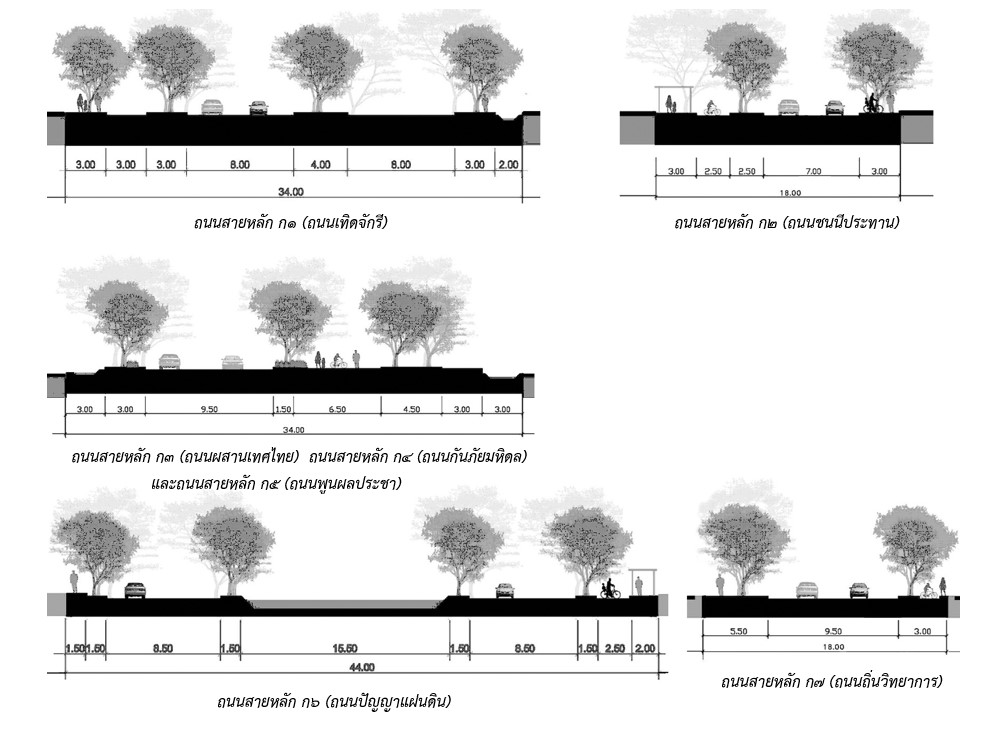
3.5 Size of Roads
Following the development of the university’s transportation system according to the 2008 Master Plan, the size of the traffic routes, main roads, secondary roads, and service roads, and internal traffic within the agency, for example:
- Main Road Kor 1 (Therd Chakri Road)
- Main Road Kor 2 (Chonni Prathan Road)
- Main Road Kor 3 (Prueng Thad Thai Road)
- Main Road Kor 4 (Kanpai Mahidol Road)
- Main road Kor 5 (Phunphon Pracha Road)
- Main Road Kor 6 (Panya Din Road)
- Main Road Kor 7 (Thin Wittayakan Road)
3.6 Internal Mass Transit System (Shuttle Buses)
The main idea of organizing a public transport system to reduce the use of cars within the university along with supporting walking and cycling.
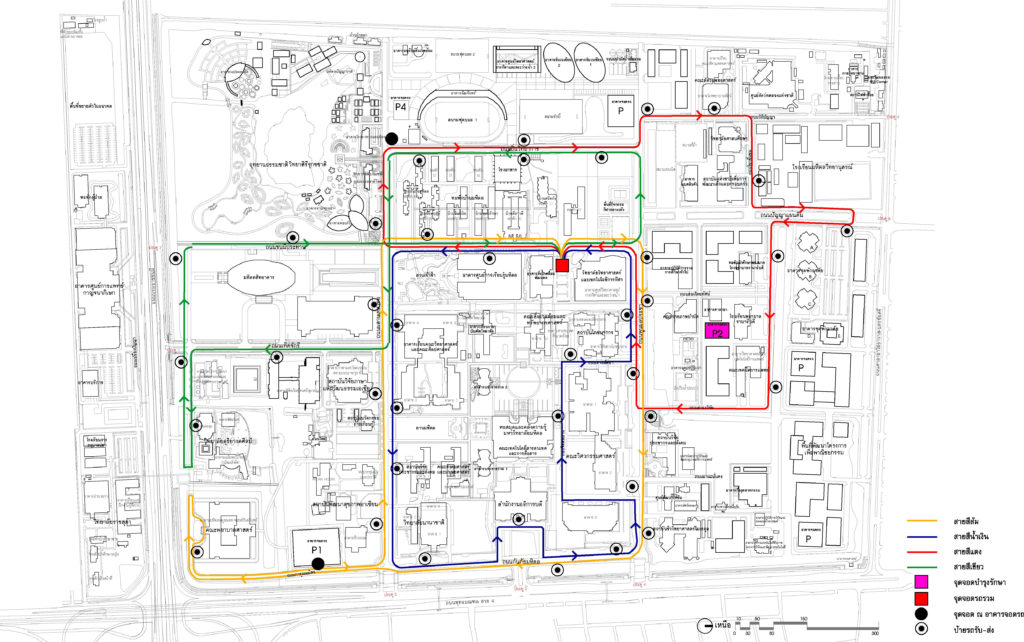
Plan showing public transport routes
-
- Development of Public Utility Systems
Development of public utilities include electric power systems sanitary system, service centers, communication systems, telephone system, waste management system and the concept of a drainage system. These to help support the development of the area in the future taking into account the reduction of energy consumption, environmental protection, reducing the use of resources within the university, valuable and efficient use of resources, which set an example for the community.
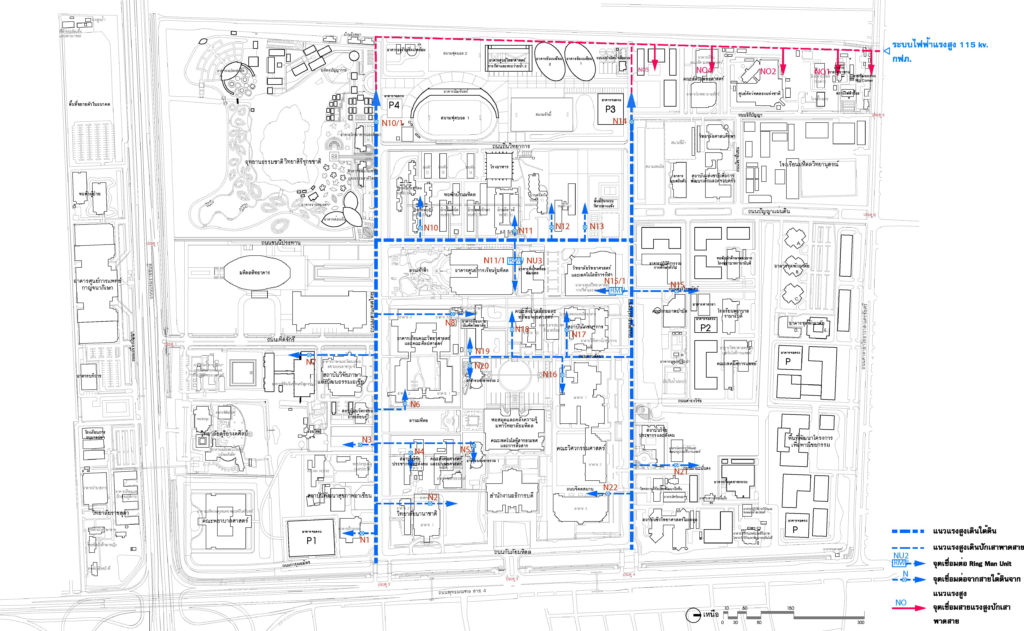
Electrical System Layout
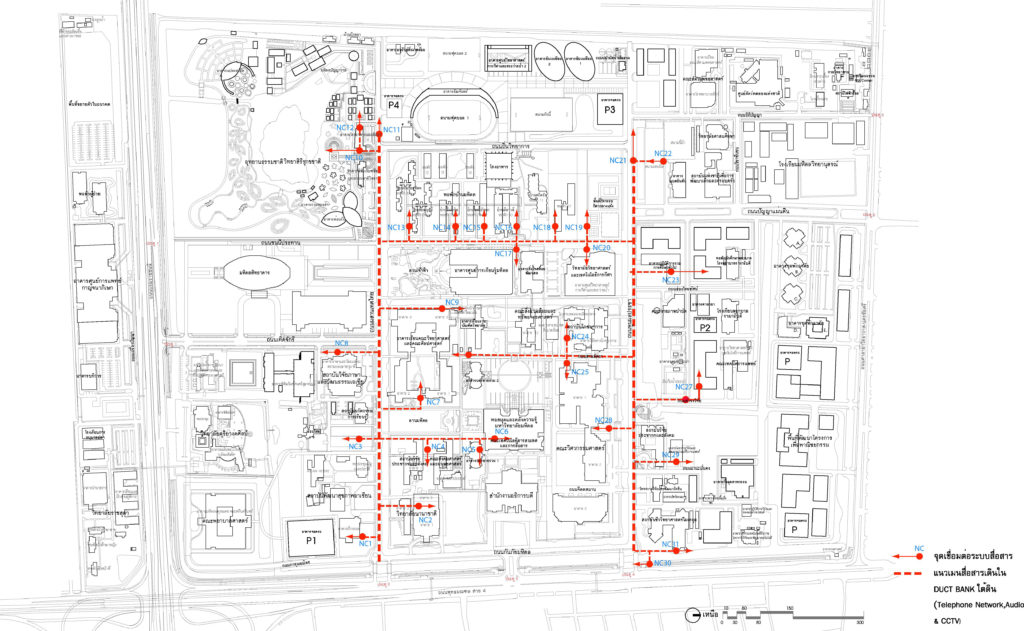
Main Layout DUCT BANK Communication System
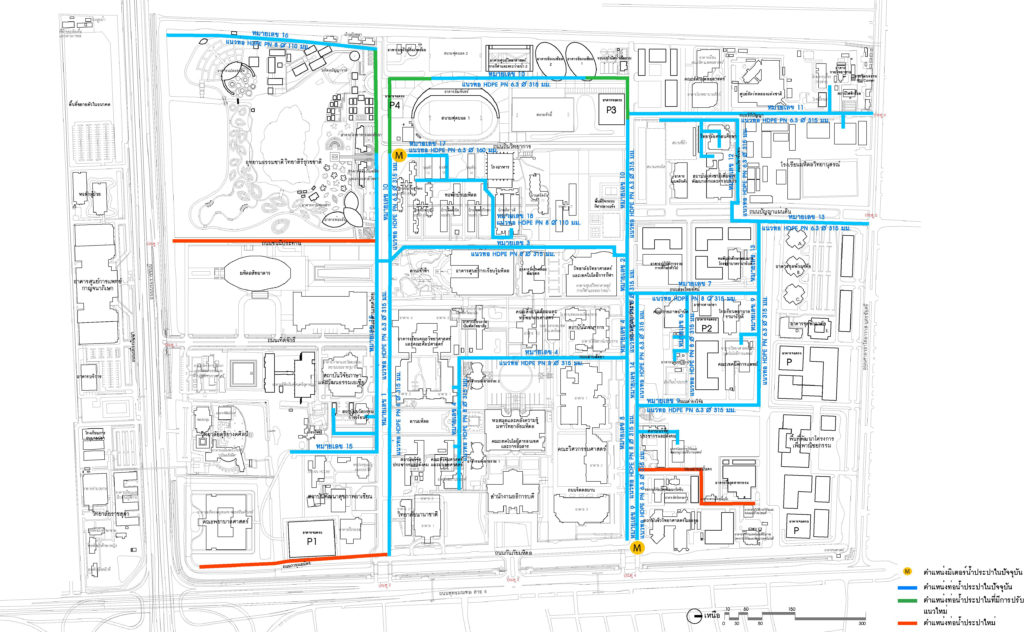
Diagram showing the water supply piping system
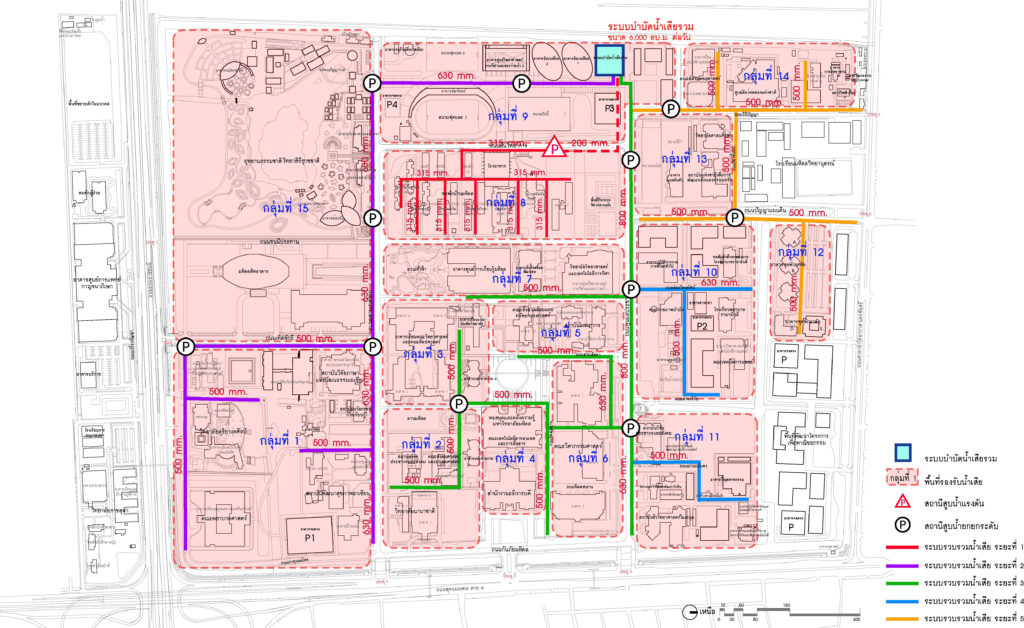
Flowchart showing the idea of improving wastewater treatment system
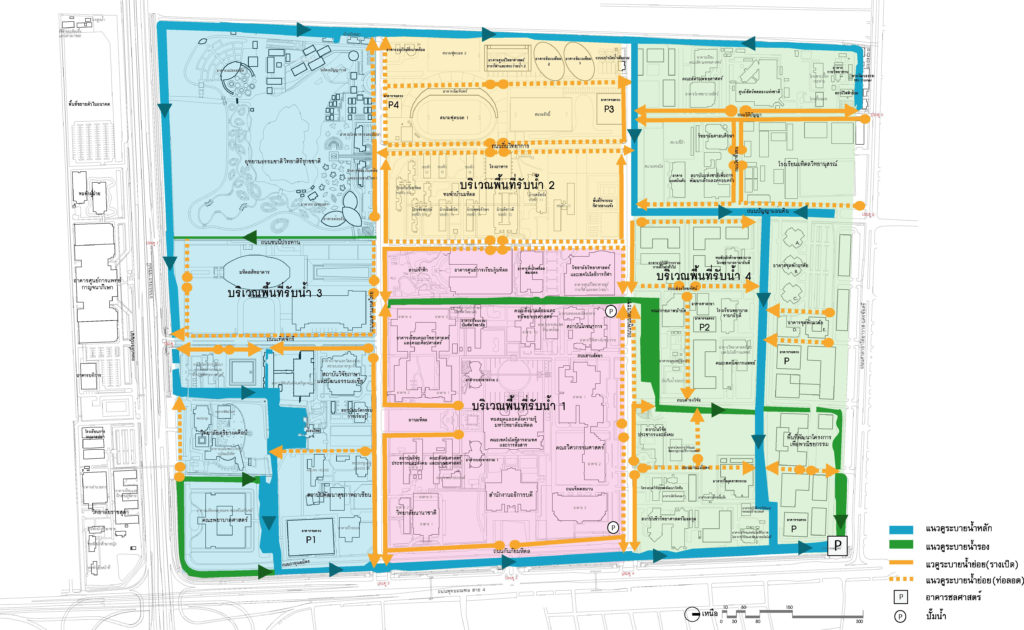 Plan showing the concept of improvement of the rainwater + flood protection system
Plan showing the concept of improvement of the rainwater + flood protection system
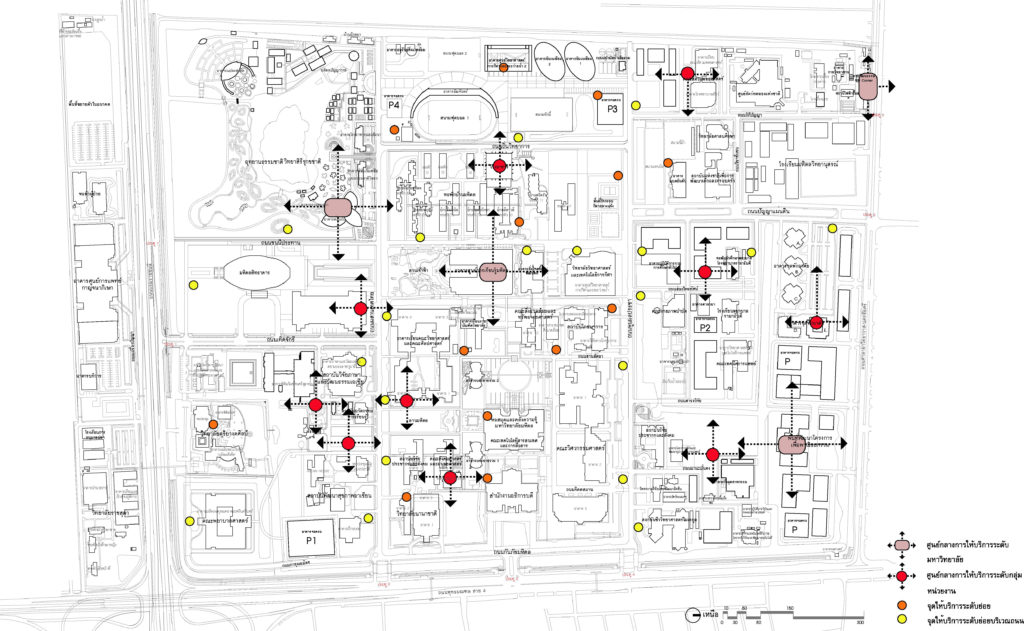
Plan showing public service points within the university
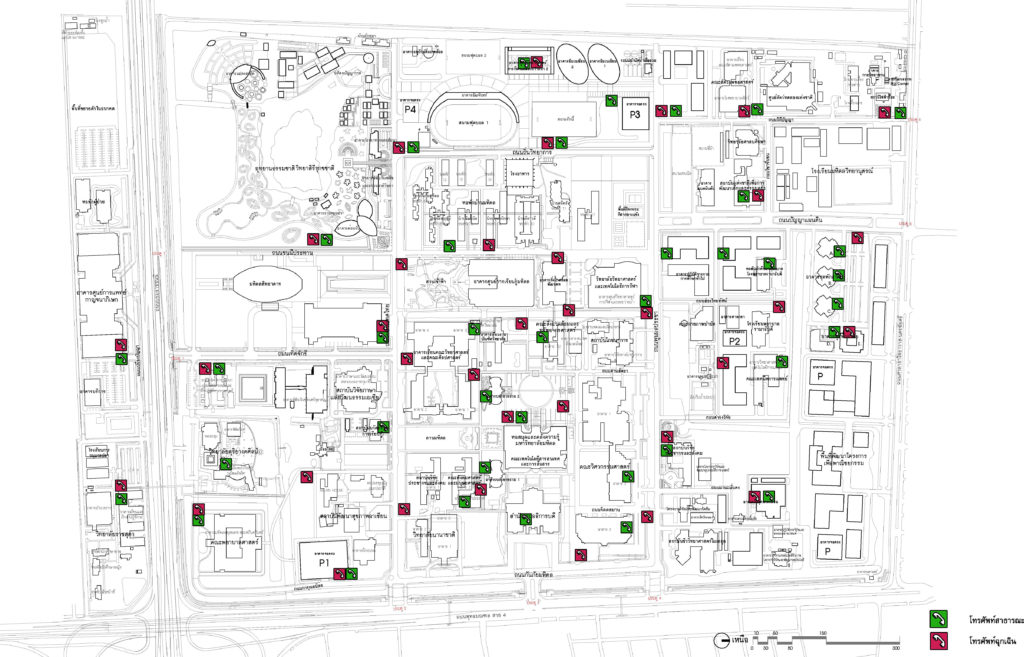
Chart showing public and emergency telephones
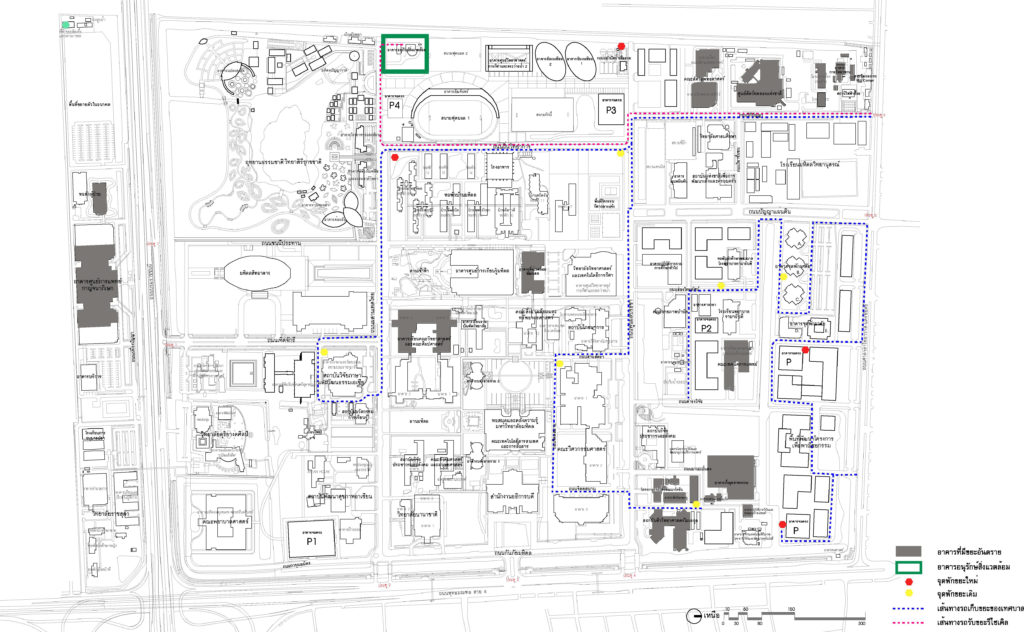
Map showing the route of the garbage truck and the garbage stop.
-
- Building and Construction Control
To support the expansion of future buildings, a system of building and construction planning has been developed to have efficient and appropriate land use for the building’s appearance, to be consistent with surrounding buildings for aesthetic reasons and to reduce building congestion in the area. There are designated building and exits to the building, services, views, and traffic from the inside to the outside of the building to connect nature with the building as one by defining the rules on the occurrence of buildings and future building design as follows:
5.1 Building layout
The future building of the future plan needs to take into consideration the attributes of the building plan, such as the opening views, the open spaces, the building styles, etc. for an ambiance of learning and connection.
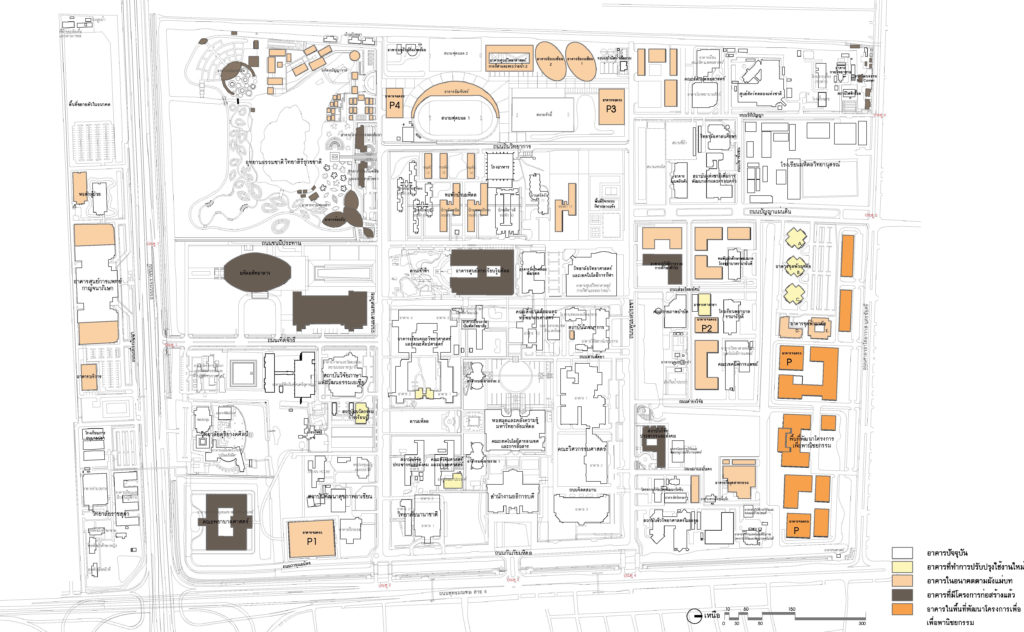
Plan showing the building construction plan according to the master plan
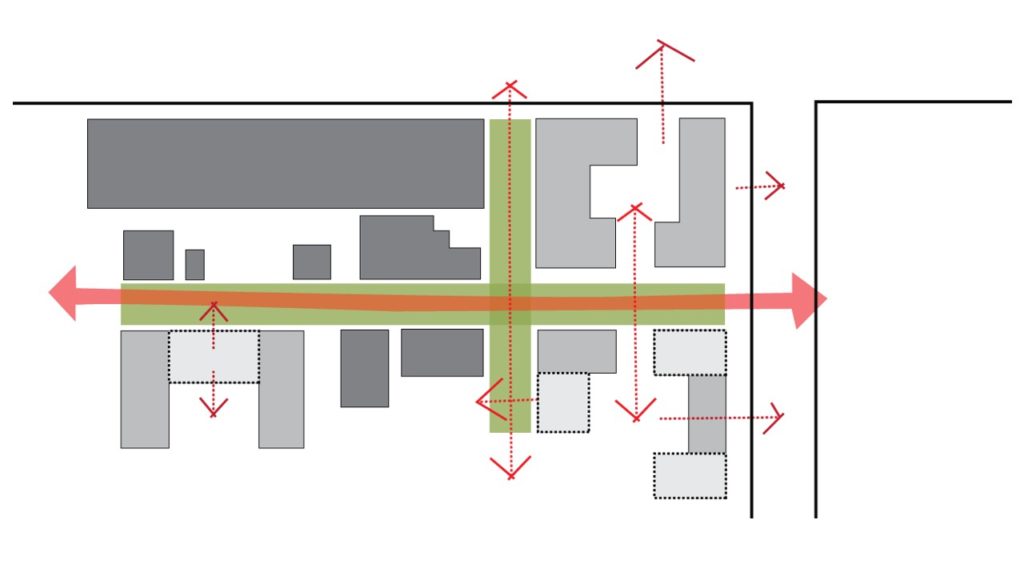
Example showing plan opening the ground floor open to the surrounding empty space.
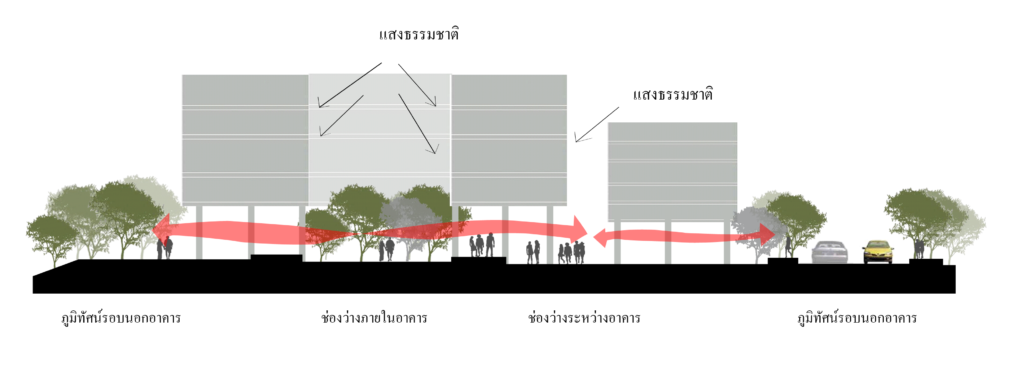
Preview showing the space between the building and the landscape around the building.
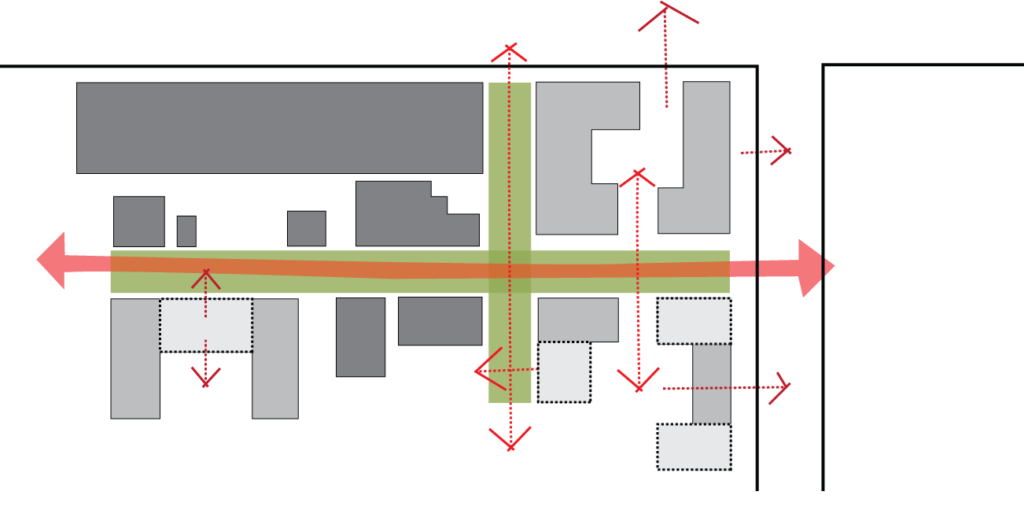
Preview showing the blank and open spaces.
5.2 Building Height
Guideline for building height control by considering each area, context, neighboring buildings to prevent problems caused by high-rise buildings obscuring the scenery of the university and comply with the law.
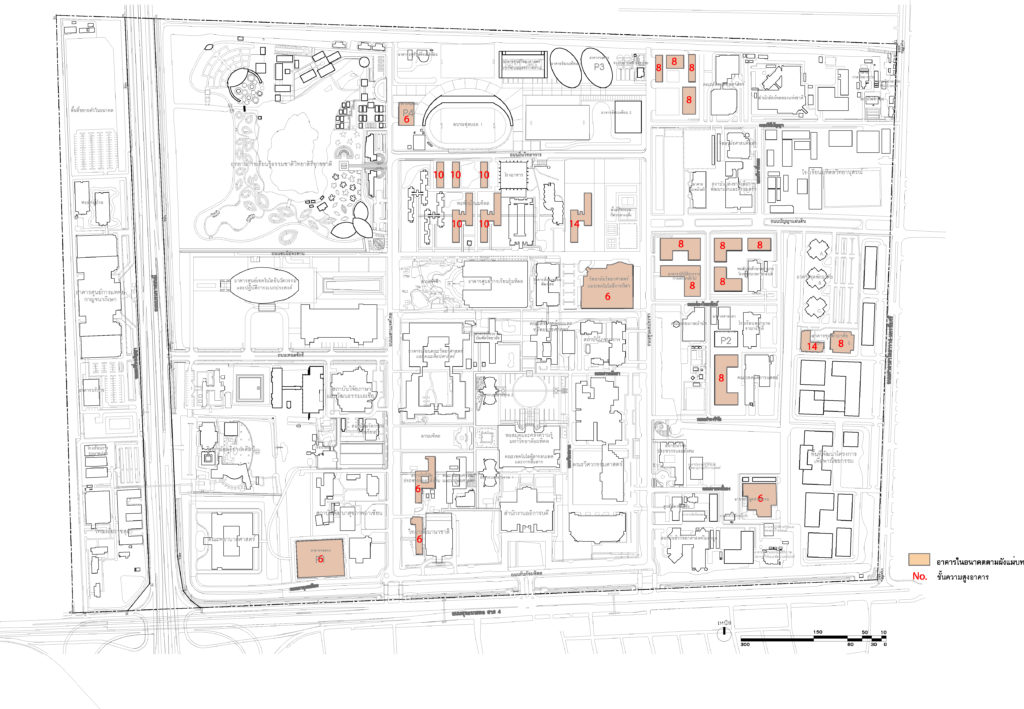
Determination of the height (number of floors) of the new building according to the master plan
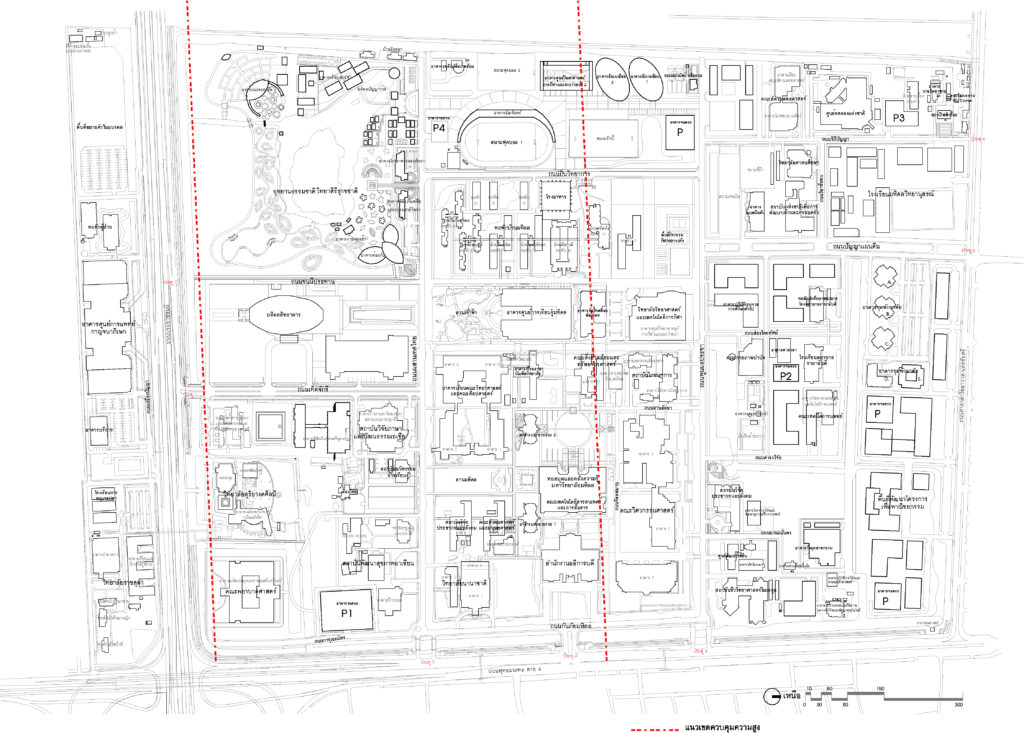
Building height control area Within Mahidol University Salaya according to the Ministerial Regulation B.E. 2549
5.3 Building Retreat Phase
Building’s retreat line is determined to create orderliness of the building line to be in continuity with the original building, prevent building congestion problems, and open space to allow the building to get more natural light, expand perspective, and increased activity area.
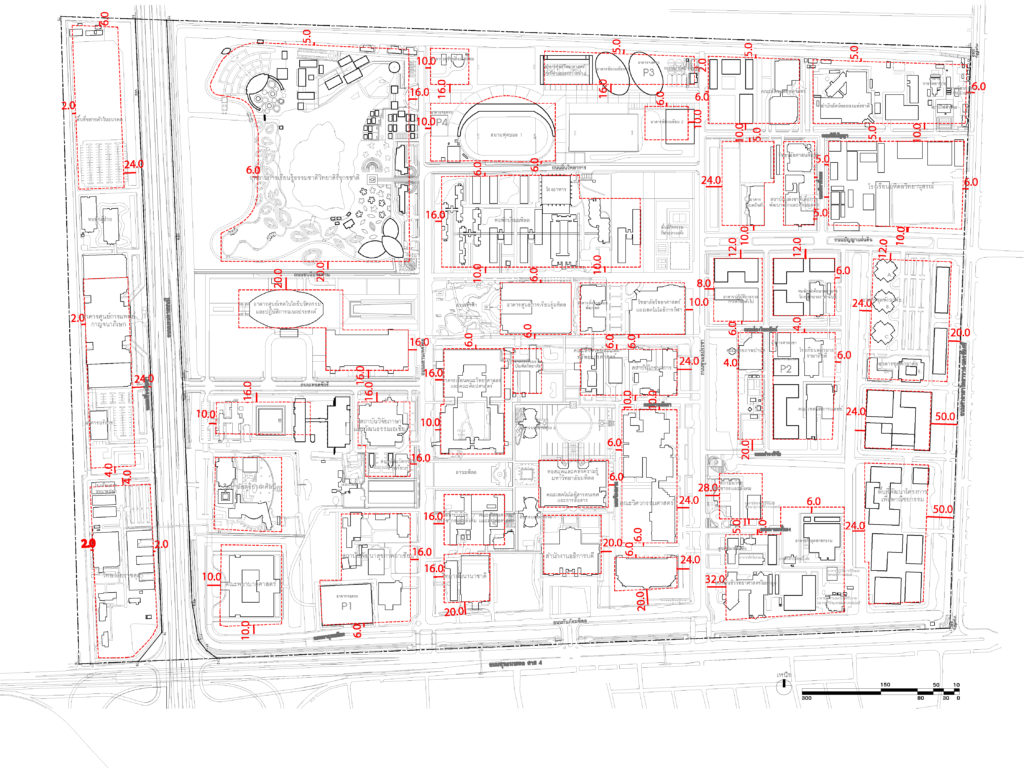
Building Retreat Line Plan
5.4 Shortening Distance between Buildings
Further development and expansion in the future need more building construction areas and at the same time, free space between buildings is required for good environmental quality. Therefore, it should be determined according to the appropriateness of the activities of the land-use area and the need to increase environmental quality by the distance between the buildings, which the minimum distance should not be less than 8 meters.
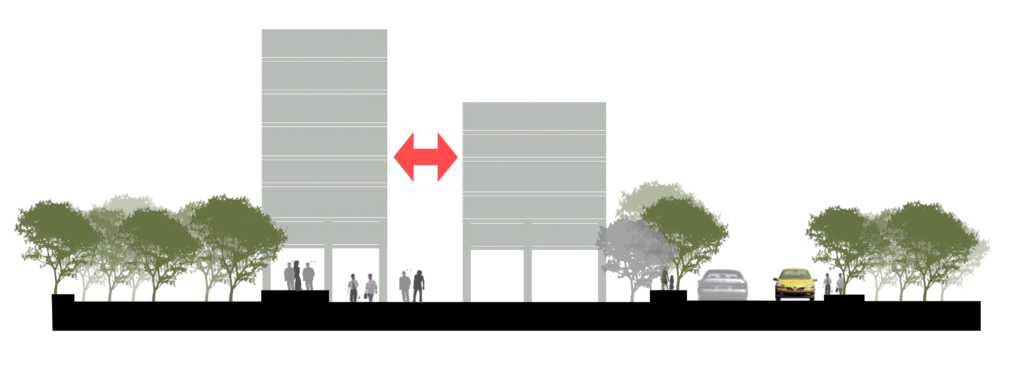
Show distance between buildings
Mahidol University Salaya Master Plan 2008 in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Goal 3 Activities areas related to health promotion, sanitation, sports, exercise, and well-being (safety of life and property).
Goal 4 Areas of activities or projects that promote equal education providing knowledge/training to outsiders and facility services for teaching.
Goal 6 Activities areas or projects on water management, wastewater and water pollution, saving/reducing water usage, water conservation, water adoption or sustainable irrigation and water security
Goal 7 Areas for activities or projects that promote energy efficiency energy saving, alternative energy, clean energy, promote low-carbon technology, or reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Goal 12: Activities or projects in the area of resource utilization, waste management, and selection of environmentally friendly products.
Goal 13 Disaster management activities or projects reducing greenhouse gas emissions-reducing global warming and climate change
Goal 14 Activity areas or projects on the use or conservation of aquatic ecosystems, and effluent quality control
Goal 15 Areas for utilization and conservation of terrestrial ecosystems, biodiversity endemic animals, and sustainable tourism.







