Efficiency of Solar Greenhouse Dryer for Drying Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes).
Faculty of Environment and Resource Studies, Mahidol University



Efficiency of Solar Greenhouse Dryer for Drying Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes).
Faculty of Environment and Resource Studies, Mahidol University
Research Title:
Efficiency of Solar Greenhouse Dryer for Drying Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes).
Researcher (s):
Phatchareephon Niroka
Lect. Dr.Gunn Panprayun
Lect. Dr.Piangjai Peerakiatkhajohn
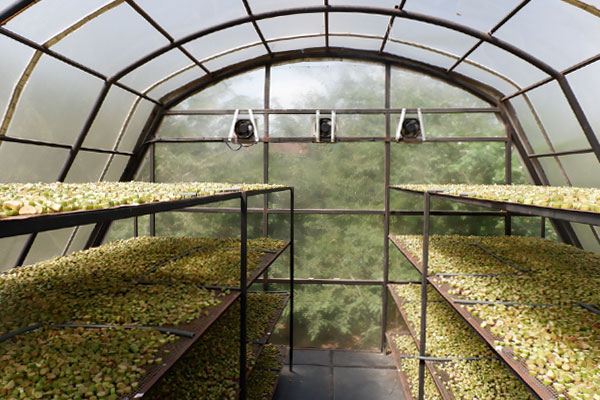
It has been several studied to utilize and reduce amount of water hyacinth due to the problem of rapid growth of water hyacinth. The community enterprise Nara Phirom group network has produced dried water hyacinth as an animal bedding for National Laboratory Animal Center, Mahidol University. However, the natural sun drying provides low quality. The growth of fungus makes the product with black spot owing to it depends on the weather factors. Therefore, this research has designed and constructed a solar greenhouse dryer for drying water hyacinth, to replace the imported bedding materials, make local income, and solve aquatic ecosystem problem. Which using high potential of renewable energy sources, to replace fossil fuels for drying or dehumidifying of product. The solar dryer located in community enterprise Nara Phirom group network, Khlong Yong Sub-district, Phutthamonthon District, Nakhon Pathom, Thailand. It consists of a parabolic roof structure covered with polycarbonate sheets. The solar dryer basement is a high platform of black metal sheet with 2-inch thick foam insulation covering a 20 m2 base area. Three ventilation fans powered by 100-W solar cell modules with a 0.54 kWh battery were installed on the top of the dryer. The fans operated to keep the relative humidity in range of the desired conditions. Two sensors were used to regulate ventilators and installed on both the inside and outside of the dryer. The fans will be operated when the relative humidity in range of the set conditions. The results of this study demonstrated that the present drying system has an overall efficiency of 78% for 100 kg of water hyacinth. After installation the relative humidity control set, the drying time was reduced and the drying rate could be increased by 0.5 times when taking out the dried sample and replace the new sample in that shelf. It provides high drying rate and less drying time than natural sun drying. The solar dryer has minimum drying time is 8 hours, while the natural sun drying is 12 hours. Moreover, the dried water hyacinth product in this dryer showed better quality of color and shape than the natural sun drying. Owing to the efficient environmental factors controlling in the drying process especially the climatic conditions, dust contamination, and insect disturbance.
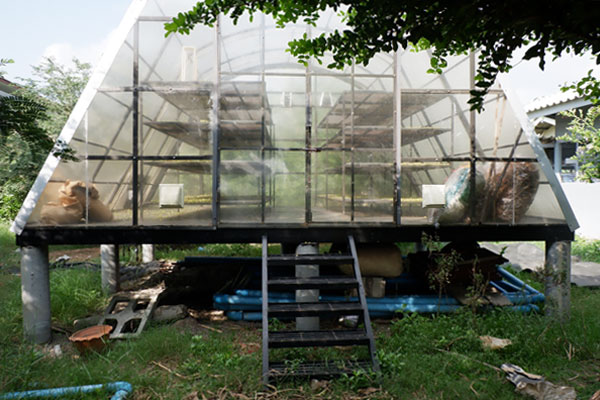
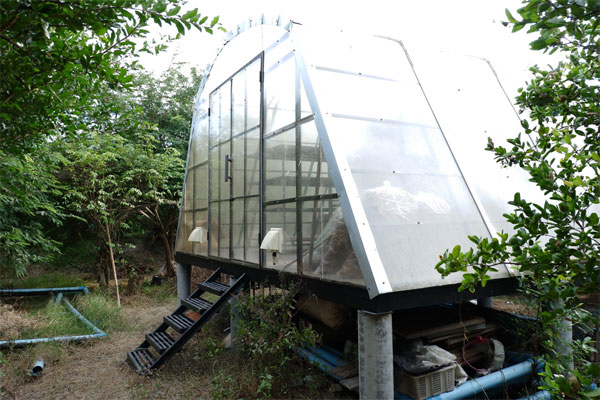
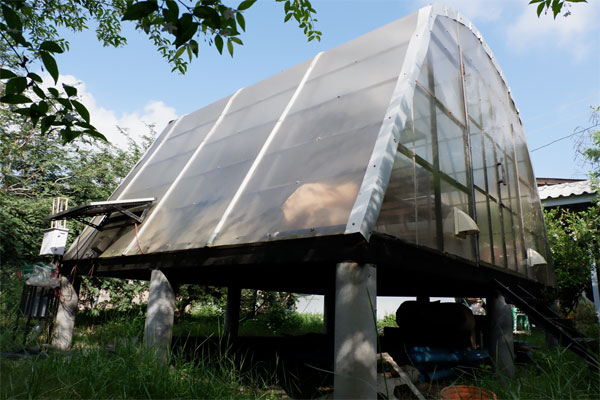
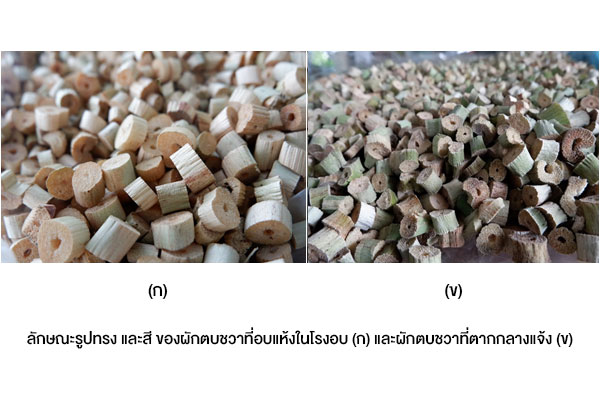




Utilization from Research: The knowledge from this research is a useful guideline for design and construction solar greenhouse dryer in the communities. To use for drying water hyacinth or another product, which make a career and income for local in another way. It also promotes the use of renewable energy sources to replace fossil fuels for drying or dehumidifying of product.
Publishing:
• P., Panprayun, G., & Peerakiatkhajohn, P. (2018, June). A Study on Efficiency of Solar Greenhouse Dryer for Drying Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). 14th Conference on Energy Network of Thailand: Modern Energy for Smart City, Thailand.
Key Contact Person:
Phatchareephon Niroka
09 4290 6219
phatchareephon.nir@gmail.com
Dr.Gunn Panprayun
0 2441 5000 ต่อ 2215
gunn.pan@mahidol.ac.th
Faculty of Environment and Resource Studies, Mahidol University