Research Highlights

Custom – Mold Silicone Toe Separator on Hallux Valgus
October 11, 2017
GMP Antimicrobial Air Spray (Antimicrobial Products from Mangosteen Extracts (Air Spray, Mouth Wash and Air Filter))
October 11, 2017Rapid Melioidosis – ICT (Rapid Immunochromatography Test for Melioidosis)
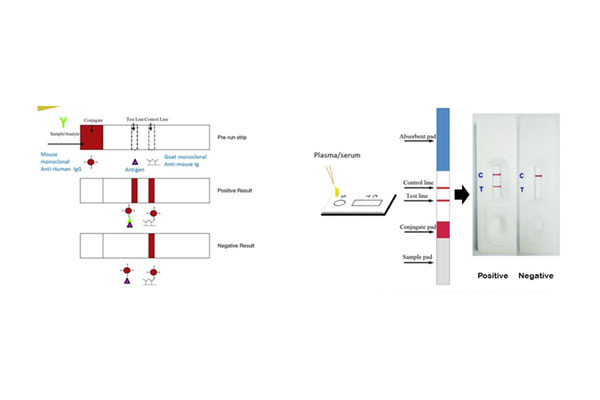
Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University


Melioidosis is caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei, soil-borne and water-borne bacteria, one of the severe infectious diseases in Thailand and other tropical countries. Specifically, in the Northeastern part of Thailand, the death rate of patients who infected with these bacteria is as high as 40%, third rank among all infectious diseases. The patients were often found in the severe cases and passed away suddenly.
This research project will benefit mostly the diagnosis of melioidosis. The physicians can, then, choose the correct antibiotic drugs, which imply for the reduction of the death rate. The development of the prototype of this diagnostic kit is based on the functioning of Hcp1, the optimal condition of this antigen, the physical characteristics of membrane composition and the testing of various solutions.
The sensitivity and specificity of this Rapid Melioidosis-ICT are 90.1% and 98.3%, respectively. When the specimens were collected from healthy human volunteers (human subjects were US and Thai citizen, pool of 100% and 83.5%), the results from Rapid Melioidosis-ICT were comparable to those from ELISA.
This Rapid Melioidosis-ICT was, therefore, one of the antibody tests that can be effectively used in the endemic area. The test took approximately 15 minutes to yield the result. It can be kept at the room temperature for 1 year, and used with different types of specimens, including serum, plasma and whole blood.
This research project will benefit mostly the diagnosis of melioidosis. The physicians can, then, choose the correct antibiotic drugs, which imply for the reduction of the death rate.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Narisara Chantratita
Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University
